
IPCS INTERNATIONAL PROGRAMME ON CHEMICAL SAFETY
Health and Safety Guide No. 82
CARBENDAZIM
HEALTH AND SAFETY GUIDE
UNITED NATIONS ENVIRONMENT PROGRAMME
INTERNATIONAL LABOUR ORGANISATION
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION, GENEVA 1993
This is a companion volume to Environmental Health Criteria
149: Carbendazim
Published by the World Health Organization for the International
Programme on Chemical Safety (a collaborative programme of the
United Nations Environment Programme, the International Labour
Organisation, and the World Health Organization)
This report contains the collective views of an international group
of experts and does not necessarily represent the decisions or the
stated policy of the United Nations Environment Programme, the
International Labour Organisation, or the World Health Organization
WHO Library Cataloguing in Publication Data
Carbendazim : health and safety guide.
(Health and safety guide ; no. 82)
1.Benzimidazoles - standards 2.Benzimidazoles - toxicity
3.Fungicides, Industrial - standards 4.Fungicides, Industrial - toxicity
I.Series
ISBN 92 4 151082 X (NLM Classification: WA 240)
ISSN 0259-7268
The World Health Organization welcomes requests for permission to
reproduce or translate its publications, in part or in full.
Applications and enquiries should be addressed to the Office of
Publications, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, which
will be glad to provide the latest information on any changes made
to the text, plans for new editions, and reprints and translations
already available.
(c) World Health Organization 1993
Publications of the World Health Organization enjoy copyright
protection in accordance with the provisions of Protocol 2 of the
Universal Copyright Convention. All rights reserved.
The designations employed and the presentation of the material in
this publication do not imply the expression of any opinion
whatsoever on the part of the Secretariat of the World Health
Organization concerning the legal status of any country, territory,
city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation
of its frontiers or boundaries.
The mention of specific companies or of certain manufacturers'
products does not imply that they are endorsed or recommended by the
World Health Organization in preference to others of a similar
nature that are not mentioned. Errors and omissions excepted, the
names of proprietary products are distinguished by initial capital
letters.
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
1. PRODUCT IDENTITY AND USES
1.1. Identity
1.2. Physical and chemical properties
1.3. Analytical methods
1.4. Production and uses
2. SUMMARY AND EVALUATION
2.1. Exposure
2.2. Uptake, metabolism, and excretion
2.3. Effects on organisms in the environment
2.4. Effects on experimental animals and in vitro
test systems
2.5. Effects on humans
3. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
4. HUMAN HEALTH HAZARDS, PREVENTION
AND PROTECTION, EMERGENCY ACTION
4.1. Human health hazards, prevention and
protection, first aid
4.1.1. Advice to physicians
4.1.2. Health surveillance advice
4.2. Explosion and fire hazards
4.3. Storage
4.4. Transport
4.5. Spillage
4.6. Disposal
5. HAZARDS FOR THE ENVIRONMENT AND THEIR PREVENTION
6. SUMMARY OF CHEMICAL SAFETY INFORMATION
7. CURRENT REGULATIONS, GUIDELINES, AND STANDARDS
7.1. Previous evaluations by international bodies
7.2. Exposure limit values
7.3. Specific restrictions
7.4. Labelling, packaging, and transport
7.5. Waste disposal
BIBLIOGRAPHY
INTRODUCTION
The Environmental Health Criteria (EHC) monographs produced by the
International Programme on Chemical Safety include an assessment of
the effects on the environment and on human health of exposure to a
chemical or combination of chemicals, or physical or biological
agents. They also provide guidelines for setting exposure limits.
The purpose of a Health and Safety Guide is to facilitate the
application of these guidelines in national chemical safety
programmes. The first three sections of a Health and Safety Guide
highlight the relevant technical information in the corresponding
EHC. Section 4 includes advice on preventive and protective measures
and emergency action; health workers should be thoroughly familiar
with the medical information to ensure that they can act efficiently
in an emergency. The section on regulatory information has been
extracted from the legal file of the International Register of
Potentially Toxic Chemicals (IRPTC) and from other United Nations
sources.
The target readership includes occupational health services, those
in ministries, governmental agencies, industry, and trade unions who
are involved in the safe use of chemicals and the avoidance of
environmental health hazards, and those wanting more information on
this topic. An attempt has been made to use only terms that will be
familiar to the intended user. However, sections 1 and 2 inevitably
contain some technical terms. A bibliography has been included for
readers who require further background information.
Revision of the information in this Guide will take place in due
course, and the eventual aim is to use standardized terminology.
Comments on any difficulties encountered in using the Guide would be
very helpful and should be addressed to:
The Director
International Programme on Chemical Safety
World Health Organization
1211 Geneva 27
Switzerland
1. PRODUCT IDENTITY AND USES
1.1 Identity
Common name: Carbendazim
Chemical formula: C9H9N3O2
Chemical structure:
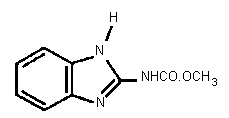 Common trade names
(including formulations): Carbendazim, Delsene, Bavistin,
Corbel, Konker, Bedazim, Derosal,
Kombat, Kemdazin, Carbendor, Hoe
017411, Cekudazim, Equitdazin,
Aimcozim (some are formulations with
other pesticides)
CAS chemical name: Methyl (1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate
Synonyms: Carbendazol (ZMAF), methyl-2-
benzimidazole carbamate (MBC, MCB,
BCM, BMC)
CAS registry number: 10605-21-7
RTECS registry number: DD 6500000
Other information: Carbendazim is a metabolite of other
benzimidazole fungicides
1.2 Physical and chemical properties
Carbendazim, a white crystalline solid, is a systemic fungicide of
the benzimidazole family. It melts at approximately 250 °C and has a
vapour pressure of <1 × 10-9 mbar at 25 °C. Carbendazim is
essentially insoluble in water (8 mg/litre) at pH 7 and 25 °C. It is
stable under normal storage conditions.
1.3 Analytical methods
Analyses of environmental samples and residues are performed by
extraction with an organic solvent and purification of the extract
by a liquid-liquid partitioning procedure. Residue levels may be
determined by HPLC or immunoassay.
1.4 Production and uses
In 1988, the estimated global sale of carbendazim was approximately
3600 tonnes. It is the most widely used member of a family of
fungicides known as the benzimidazoles. Carbendazim is a systemic
and broad spectrum fungicide that is currently registered for use
for the control of diseases in fruit trees, nut crops, vegetables,
cereals, tropical crops and ornamentals, turf, and many field crops.
It is formulated as an aqueous dispersion, aqueous suspension,
flowable water dispersible granules, and a wettable powder.
2. SUMMARY AND EVALUATION
2.1 Exposure
The primary source of carbendazim exposure for the general human
population is dietary intake. Estimated human exposures, based on
dietary analysis and crop tolerance values, indicate an expected
intake substantially below the recommended Acceptable Daily Intake
(ADI), based on no-observed-effect levels in animal tests.
Occupational exposure during manufacture or crop application is
within acceptable levels. Primary routes of exposure are inhalation
and dermal contact and both are easily reduced and controlled by the
use of dust masks and protective clothing.
2.2 Uptake, metabolism, and excretion
Carbendazim is well absorbed after oral, but not dermal, exposure.
Absorbed carbendazim is rapidly metabolized and eliminated in the
urine and faeces.
2.3 Effects on organisms in the environment
Because of its stability on plant material, lasting several weeks,
carbendazim may become accessible to organisms feeding on leaf
litter. Soil and sediments may contain residues of carbendazim for
up to 3 years. However, the strong adsorption of carbendazim on soil
and sediment particles reduces the exposure of terrestrial and
aquatic organisms.
Carbendazim applied at recommended application rates has little
effect on soil microbial activity. Some adverse effects have been
reported in groups of fungi.
Carbendazim is algicidal and was toxic for aquatic organisms and
fish in laboratory studies.
Carbendazim was toxic for earthworms in laboratory studies, when
applied at realistic exposure concentrations, and, in the field, at
recommended levels of use. Its toxicity for birds is low and it is
relatively non-toxic for honey bees.
2.4 Effects on experimental animals and in vitro test systems
The toxicity of carbendazim through ingestion is low, with an LD50
in rats of 10 000 mg/kg. Inhalation toxicity is very low (4-h LC50
>50 mg/litre) and toxicity through dermal contact, moderate (LD50
>10 000 mg/kg). Carbendazim is not a skin irritant or sensitizer in
guinea-pigs, but it may cause eye irritation.
In long-term feeding studies on rats, hepatotoxicity and testicular
toxicity were observed at dose levels greater than 500 mg/kg
(equivalent to 25 mg/kg body weight per day). Hepatotoxicity was
observed in dogs at dose levels greater than 300 mg/kg. Decreases in
sperm counts and reduced fertility were found in rats at dose levels
of 50 mg/kg body weight per day or more. No effect on the male
reproductive system was found at a dose level of 500 mg/kg (25 mg/kg
body weight per day) in the rat.
Carbendazim caused increases in malformations and anomalies in the
rat at dose levels greater than 10 mg/kg. Decreases in fetal weight
and increases in fetal lethality were also found in the rat at dose
levels of 20 mg/kg body weight per day or more.
Carbendazim resulted in an increased incidence of hepatocellular
tumours in certain strains of mice known to have a high background
rate for these tumours. No carcinogenic effect was observed in rats.
Carbendazim is not a heritable gene mutagen. However, it produced
numerous chromosome aberrations or aneuploidy, caused by the same
mechanism that is responsible for its fungicidal activity.
Carbendazim was found to bind to fungal tubulin but to have a low
affinity for mammalian tubulin.
2.5 Effects on humans
No inadvertent poisoning of agricultural or factory workers has been
documented.
3. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Estimated human exposures, based on dietary analysis and crop
tolerance values, indicate the expected intake to be below the
recommended Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI), based on
no-observed-effect levels in animal tests. Given the toxicity levels
of carbendazim and the low dietary exposure levels, it is unlikely
that it poses a significant health risk for the general population.
Occupational exposures during manufacture or crop application are
below the established Threshold Limit Values.
Carbendazim is strongly adsorbed on soil organic matter and persists
in the soil for up to 3 years. Carbendazim persists on leaf surfaces
and, therefore, in leaf litter. Earthworms have been shown to be
adversely affected (population and reproductive effects) at
recommended rates of application. There is no information on other
soil or litter arthropods that would be similarly exposed.
The high toxicity for aquatic organisms in laboratory tests is
unlikely to be seen in the field, because of the low bioavailability
of sediment-bound residues of carbendazim. However, no information
is available on sediment-living species, which would receive high
exposure.
4. HUMAN HEALTH HAZARDS, PREVENTION AND PROTECTION, EMERGENCY
ACTION
4.1 Human health hazards, prevention and protection, first aid
4.1.1 Advice to physicians
The acute toxicity of carbendazim for humans is believed to be very
low. There is no specific antidote. In case of skin contact,
immediately wash skin with soap and water. In case of eye contact,
immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 min.
4.1.2 Health surveillance advice
No specific health surveillance information is available.
4.2 Explosion and fire hazards
4.2.1 Explosion hazards
Like most organic powders or crystals, under severe dust conditions,
this material may form explosive mixtures in air.
4.2.2 Fire hazards
Evacuate personnel to a safe area, keeping them away from, and
upwind of, the fire. Wear self-contained breathing apparatus. Use
water or dry chemical to extinguish the fire and water spray to cool
the tank/container.
4.3 Storage
Store in well ventilated area. Keep container tightly closed. Do not
store or consume food, drink, or tobacco in areas where they may
become contaminated with this material.
4.4 Transport
All products should be transported in secure vehicles according to
local regulations. Containers should be sound, adequately labelled,
and kept dry.
4.5 Spillage
Sections 4.1 and 4.2 of this Guide should be reviewed before
proceeding with clean up. Use appropriate personnel protective
equipment during clean up.
Prevent liquid from entering sewers, waterways, or low areas.
Shovel, or sweep, up.
4.6 Disposal
Treatment, storage, transportation, and disposal must be in
accordance with applicable local regulations. Remove nonusable solid
materials and/or contaminated soil for disposal in an approved and
permitted landfill. Do not flush into surface water or sanitary
sewer systems.
Do not reuse container; dispose of according to approved local
procedures.
5. HAZARDS FOR THE ENVIRONMENT AND THEIR PREVENTION
The strong adsorption of benomyl and its degradation product
carbendazim on particulates in soil and aquatic sediment reduces its
bioavailability. However, earthworm populations have been reduced at
recommended application rates. There is no information on toxicity
to other soil invertebrates or aquatic invertebrates living in
sediments. Residues on particulates may persist for years.
Excessive application of benomyl to the same area should be avoided
to prevent build up of residues. Disposal should avoid contamination
of both soil and surface water sediments.
6. SUMMARY OF CHEMICAL SAFETY INFORMATION
This summary should be easily available to all health workers
concerned with, and users of, carbendazim. It should be displayed
at, or near, entrances to areas where there is potential exposure to
carbendazim, and on processing equipment and containers. The summary
should be translated into the appropriate language(s). All persons
potentially exposed to the chemical should also have the
instructions in the summary clearly explained.
Space is available for insertion of the National Occupational
Exposure Limit, the address and telephone number of the National
Poison Control Centre, and local trade names.
SUMMARY OF CHEMICAL SAFETY INFORMATION
CARBENDAZIM
Methyl (1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate
C9H9N3O2
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OTHER CHARACTERISTICS
Relative molecular mass 191.2 White, crystalline solid
Melting point (°C) 250
Water solubility (mg/litre, pH 7, 25 °C) 8.0
Specific density 0.27
Relative vapour pressure (Pa, 20 °C) <1 x 10-7
Explosion limit (LEL, g/litre in air) 0.13
HAZARD/SYMPTOM PREVENTION AND PROTECTION FIRST AID
SKIN: Irritation Wear long-sleeved shirt and long Remove contaminated clothing, wash with
trousers, chemical resistant gloves, soap and water, and obtain medical
shoes or boots treatment
EYE: Irritation Wear safety goggles or face shield Flush with plenty of water for at least
15 min and obtain medical treatment
INHALATION: Irritation Avoid breathing dust or spray mist Remove from exposure; obtain medical
attention
INGESTION: Do not eat, drink, chew or smoke Obtain medical attention
during use; keep out of reach of
children
HAZARD/SYMPTOM PREVENTION AND PROTECTION FIRST AID
ENVIRONMENT: Presents a risk Contamination of water and soil
for aquatic and soil organisms should be avoided by proper methods
of application, storage, transport, and
waste disposal
SPILLAGE STORAGE FIRE AND EXPLOSION
Wear appropriate protective Store in well ventilated area; keep Under severe dust conditions, carbendazim
equipment during clean up; prevent container tightly closed; store in may form explosive mixtures in air;
liquid from entering sewers, original container only, away from in case of fire, evacuate personnel
waterways, or low areas; shovel, other pesticides, fertilizer, food, to a safe area, wear self-contained
or sweep, up or animal feed; do not allow to breathing apparatus, use water or dry
become wet during storage chemical to extinguish fire, and cool
tank/container with water spray
WASTE DISPOSAL
Treatment, storage, transportation, National occupational exposure
and disposal must be in accordance limit:
with applicable local regulations;
waste disposal must be in an
approved and permitted landfill or
by incineration; do not flush to National Poison Control Centre:
surface water or sanitary sewer
system
7. CURRENT REGULATIONS, GUIDELINES AND STANDARDS
7.1 Previous evaluations by international bodies
Carbendazim was evaluated by the Joint FAO/WHO Meeting on Pesticide
Residues (JMPR) in 1973, 1975, 1978, 1983, and 1988. The 1978
meeting agreed that the Maximum Residue Limits for benomyl,
carbendazim, and thiophanate-methyl should be combined and expressed
as carbendazim. The 1983 meeting evaluated benomyl toxicology and
set the following carbendazim no-observed-effect levels (NOELs) and
ADI:
Rat 500 mg/kg diet, equivalent to 25 mg/kg body
weight
Dog 100 mg/kg diet, equivalent to 2.5 mg/kg
body weight
Rat (teratology) 30 mg/kg body weight per day (benomyl).
The estimated ADI for carbendazim was established at 0-0.01 mg/kg
body weight.
7.2 Exposure limit values
Exposure limit values are presented in the table on p. 20.
7.3 Specific restrictions
There are no specific restrictions on the use of carbendazim.
7.4 Labelling, packaging, and transport
European Economic Community legislation requires labelling as a
dangerous substance using the symbol Xn.
Common trade names
(including formulations): Carbendazim, Delsene, Bavistin,
Corbel, Konker, Bedazim, Derosal,
Kombat, Kemdazin, Carbendor, Hoe
017411, Cekudazim, Equitdazin,
Aimcozim (some are formulations with
other pesticides)
CAS chemical name: Methyl (1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate
Synonyms: Carbendazol (ZMAF), methyl-2-
benzimidazole carbamate (MBC, MCB,
BCM, BMC)
CAS registry number: 10605-21-7
RTECS registry number: DD 6500000
Other information: Carbendazim is a metabolite of other
benzimidazole fungicides
1.2 Physical and chemical properties
Carbendazim, a white crystalline solid, is a systemic fungicide of
the benzimidazole family. It melts at approximately 250 °C and has a
vapour pressure of <1 × 10-9 mbar at 25 °C. Carbendazim is
essentially insoluble in water (8 mg/litre) at pH 7 and 25 °C. It is
stable under normal storage conditions.
1.3 Analytical methods
Analyses of environmental samples and residues are performed by
extraction with an organic solvent and purification of the extract
by a liquid-liquid partitioning procedure. Residue levels may be
determined by HPLC or immunoassay.
1.4 Production and uses
In 1988, the estimated global sale of carbendazim was approximately
3600 tonnes. It is the most widely used member of a family of
fungicides known as the benzimidazoles. Carbendazim is a systemic
and broad spectrum fungicide that is currently registered for use
for the control of diseases in fruit trees, nut crops, vegetables,
cereals, tropical crops and ornamentals, turf, and many field crops.
It is formulated as an aqueous dispersion, aqueous suspension,
flowable water dispersible granules, and a wettable powder.
2. SUMMARY AND EVALUATION
2.1 Exposure
The primary source of carbendazim exposure for the general human
population is dietary intake. Estimated human exposures, based on
dietary analysis and crop tolerance values, indicate an expected
intake substantially below the recommended Acceptable Daily Intake
(ADI), based on no-observed-effect levels in animal tests.
Occupational exposure during manufacture or crop application is
within acceptable levels. Primary routes of exposure are inhalation
and dermal contact and both are easily reduced and controlled by the
use of dust masks and protective clothing.
2.2 Uptake, metabolism, and excretion
Carbendazim is well absorbed after oral, but not dermal, exposure.
Absorbed carbendazim is rapidly metabolized and eliminated in the
urine and faeces.
2.3 Effects on organisms in the environment
Because of its stability on plant material, lasting several weeks,
carbendazim may become accessible to organisms feeding on leaf
litter. Soil and sediments may contain residues of carbendazim for
up to 3 years. However, the strong adsorption of carbendazim on soil
and sediment particles reduces the exposure of terrestrial and
aquatic organisms.
Carbendazim applied at recommended application rates has little
effect on soil microbial activity. Some adverse effects have been
reported in groups of fungi.
Carbendazim is algicidal and was toxic for aquatic organisms and
fish in laboratory studies.
Carbendazim was toxic for earthworms in laboratory studies, when
applied at realistic exposure concentrations, and, in the field, at
recommended levels of use. Its toxicity for birds is low and it is
relatively non-toxic for honey bees.
2.4 Effects on experimental animals and in vitro test systems
The toxicity of carbendazim through ingestion is low, with an LD50
in rats of 10 000 mg/kg. Inhalation toxicity is very low (4-h LC50
>50 mg/litre) and toxicity through dermal contact, moderate (LD50
>10 000 mg/kg). Carbendazim is not a skin irritant or sensitizer in
guinea-pigs, but it may cause eye irritation.
In long-term feeding studies on rats, hepatotoxicity and testicular
toxicity were observed at dose levels greater than 500 mg/kg
(equivalent to 25 mg/kg body weight per day). Hepatotoxicity was
observed in dogs at dose levels greater than 300 mg/kg. Decreases in
sperm counts and reduced fertility were found in rats at dose levels
of 50 mg/kg body weight per day or more. No effect on the male
reproductive system was found at a dose level of 500 mg/kg (25 mg/kg
body weight per day) in the rat.
Carbendazim caused increases in malformations and anomalies in the
rat at dose levels greater than 10 mg/kg. Decreases in fetal weight
and increases in fetal lethality were also found in the rat at dose
levels of 20 mg/kg body weight per day or more.
Carbendazim resulted in an increased incidence of hepatocellular
tumours in certain strains of mice known to have a high background
rate for these tumours. No carcinogenic effect was observed in rats.
Carbendazim is not a heritable gene mutagen. However, it produced
numerous chromosome aberrations or aneuploidy, caused by the same
mechanism that is responsible for its fungicidal activity.
Carbendazim was found to bind to fungal tubulin but to have a low
affinity for mammalian tubulin.
2.5 Effects on humans
No inadvertent poisoning of agricultural or factory workers has been
documented.
3. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Estimated human exposures, based on dietary analysis and crop
tolerance values, indicate the expected intake to be below the
recommended Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI), based on
no-observed-effect levels in animal tests. Given the toxicity levels
of carbendazim and the low dietary exposure levels, it is unlikely
that it poses a significant health risk for the general population.
Occupational exposures during manufacture or crop application are
below the established Threshold Limit Values.
Carbendazim is strongly adsorbed on soil organic matter and persists
in the soil for up to 3 years. Carbendazim persists on leaf surfaces
and, therefore, in leaf litter. Earthworms have been shown to be
adversely affected (population and reproductive effects) at
recommended rates of application. There is no information on other
soil or litter arthropods that would be similarly exposed.
The high toxicity for aquatic organisms in laboratory tests is
unlikely to be seen in the field, because of the low bioavailability
of sediment-bound residues of carbendazim. However, no information
is available on sediment-living species, which would receive high
exposure.
4. HUMAN HEALTH HAZARDS, PREVENTION AND PROTECTION, EMERGENCY
ACTION
4.1 Human health hazards, prevention and protection, first aid
4.1.1 Advice to physicians
The acute toxicity of carbendazim for humans is believed to be very
low. There is no specific antidote. In case of skin contact,
immediately wash skin with soap and water. In case of eye contact,
immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 min.
4.1.2 Health surveillance advice
No specific health surveillance information is available.
4.2 Explosion and fire hazards
4.2.1 Explosion hazards
Like most organic powders or crystals, under severe dust conditions,
this material may form explosive mixtures in air.
4.2.2 Fire hazards
Evacuate personnel to a safe area, keeping them away from, and
upwind of, the fire. Wear self-contained breathing apparatus. Use
water or dry chemical to extinguish the fire and water spray to cool
the tank/container.
4.3 Storage
Store in well ventilated area. Keep container tightly closed. Do not
store or consume food, drink, or tobacco in areas where they may
become contaminated with this material.
4.4 Transport
All products should be transported in secure vehicles according to
local regulations. Containers should be sound, adequately labelled,
and kept dry.
4.5 Spillage
Sections 4.1 and 4.2 of this Guide should be reviewed before
proceeding with clean up. Use appropriate personnel protective
equipment during clean up.
Prevent liquid from entering sewers, waterways, or low areas.
Shovel, or sweep, up.
4.6 Disposal
Treatment, storage, transportation, and disposal must be in
accordance with applicable local regulations. Remove nonusable solid
materials and/or contaminated soil for disposal in an approved and
permitted landfill. Do not flush into surface water or sanitary
sewer systems.
Do not reuse container; dispose of according to approved local
procedures.
5. HAZARDS FOR THE ENVIRONMENT AND THEIR PREVENTION
The strong adsorption of benomyl and its degradation product
carbendazim on particulates in soil and aquatic sediment reduces its
bioavailability. However, earthworm populations have been reduced at
recommended application rates. There is no information on toxicity
to other soil invertebrates or aquatic invertebrates living in
sediments. Residues on particulates may persist for years.
Excessive application of benomyl to the same area should be avoided
to prevent build up of residues. Disposal should avoid contamination
of both soil and surface water sediments.
6. SUMMARY OF CHEMICAL SAFETY INFORMATION
This summary should be easily available to all health workers
concerned with, and users of, carbendazim. It should be displayed
at, or near, entrances to areas where there is potential exposure to
carbendazim, and on processing equipment and containers. The summary
should be translated into the appropriate language(s). All persons
potentially exposed to the chemical should also have the
instructions in the summary clearly explained.
Space is available for insertion of the National Occupational
Exposure Limit, the address and telephone number of the National
Poison Control Centre, and local trade names.
SUMMARY OF CHEMICAL SAFETY INFORMATION
CARBENDAZIM
Methyl (1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate
C9H9N3O2
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OTHER CHARACTERISTICS
Relative molecular mass 191.2 White, crystalline solid
Melting point (°C) 250
Water solubility (mg/litre, pH 7, 25 °C) 8.0
Specific density 0.27
Relative vapour pressure (Pa, 20 °C) <1 x 10-7
Explosion limit (LEL, g/litre in air) 0.13
HAZARD/SYMPTOM PREVENTION AND PROTECTION FIRST AID
SKIN: Irritation Wear long-sleeved shirt and long Remove contaminated clothing, wash with
trousers, chemical resistant gloves, soap and water, and obtain medical
shoes or boots treatment
EYE: Irritation Wear safety goggles or face shield Flush with plenty of water for at least
15 min and obtain medical treatment
INHALATION: Irritation Avoid breathing dust or spray mist Remove from exposure; obtain medical
attention
INGESTION: Do not eat, drink, chew or smoke Obtain medical attention
during use; keep out of reach of
children
HAZARD/SYMPTOM PREVENTION AND PROTECTION FIRST AID
ENVIRONMENT: Presents a risk Contamination of water and soil
for aquatic and soil organisms should be avoided by proper methods
of application, storage, transport, and
waste disposal
SPILLAGE STORAGE FIRE AND EXPLOSION
Wear appropriate protective Store in well ventilated area; keep Under severe dust conditions, carbendazim
equipment during clean up; prevent container tightly closed; store in may form explosive mixtures in air;
liquid from entering sewers, original container only, away from in case of fire, evacuate personnel
waterways, or low areas; shovel, other pesticides, fertilizer, food, to a safe area, wear self-contained
or sweep, up or animal feed; do not allow to breathing apparatus, use water or dry
become wet during storage chemical to extinguish fire, and cool
tank/container with water spray
WASTE DISPOSAL
Treatment, storage, transportation, National occupational exposure
and disposal must be in accordance limit:
with applicable local regulations;
waste disposal must be in an
approved and permitted landfill or
by incineration; do not flush to National Poison Control Centre:
surface water or sanitary sewer
system
7. CURRENT REGULATIONS, GUIDELINES AND STANDARDS
7.1 Previous evaluations by international bodies
Carbendazim was evaluated by the Joint FAO/WHO Meeting on Pesticide
Residues (JMPR) in 1973, 1975, 1978, 1983, and 1988. The 1978
meeting agreed that the Maximum Residue Limits for benomyl,
carbendazim, and thiophanate-methyl should be combined and expressed
as carbendazim. The 1983 meeting evaluated benomyl toxicology and
set the following carbendazim no-observed-effect levels (NOELs) and
ADI:
Rat 500 mg/kg diet, equivalent to 25 mg/kg body
weight
Dog 100 mg/kg diet, equivalent to 2.5 mg/kg
body weight
Rat (teratology) 30 mg/kg body weight per day (benomyl).
The estimated ADI for carbendazim was established at 0-0.01 mg/kg
body weight.
7.2 Exposure limit values
Exposure limit values are presented in the table on p. 20.
7.3 Specific restrictions
There are no specific restrictions on the use of carbendazim.
7.4 Labelling, packaging, and transport
European Economic Community legislation requires labelling as a
dangerous substance using the symbol Xn.
 Table 1. Exposure limit values
Medium Specification Country/ Exposure limit Values
organization description
Food plant (specified) Brazil Acceptable limit (AL) 0.1-0.5 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) Germany Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.2-7.0 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) India Maximum tolerable concentration (MTC) 0.1-5.0 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) Russian Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1 mg/kg
Federation
Food cereals Sweden Maximum tolerable concentration (MTC) 0.1 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) United Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1-10.0 mg/kg
Kingdom
Food FAO Acceptable daily intake (ADI) 0.02 mg/kg body weight
Food plant (specified) FAO Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1-50 mg/kg
Air occupational Russian Maximum allowable concentration (MAC) 0.1 mg/m3
(aerosol) Federation
Water surface water Russian Maximum allowable concentration (MAC) 0.1 mg/litre
Federation
a From: IRPTC Legal File (1992).
The following label statements are required:
R40 - Possible risk of irreversible effects
S36/37 - Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves
Carbendazim has been classified as a Marine Pollutant and a
Flammable Solid by the International Maritime Organization.
7.5 Waste disposal
European Economic Community regulations require that carbendazim
and/or its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
FAO/WHO (1985a) Benomyl. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1983:
evaluations 1983. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 7-46.
FAO/WHO (1985b) Carbendazim. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1983:
evaluations 1983. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 89-121.
FAO/WHO (1988a) Benomyl. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1988:
evaluations 1988. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 5-15.
FAO/WHO (1988b) Carbendazim. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1988:
evaluations 1988. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 41-54.
ILO (1991) Occupational exposure limits for airborne toxic
substances. Geneva, International Labour Organisation
(Occupational Safety and Health Series, No. 37).
UNEP IRPTC (1992) IRPTC legal file 1992. Geneva, International
Register of Potentially Toxic Chemicals, United Nations Environment
Programme.
WHO (1993) Environmental Health Criteria 148: Benomyl. Geneva,
World Health Organization.
WHO (1993) Environmental Health Criteria 149: Carbendazim. Geneva,
World Health Organization.
Table 1. Exposure limit values
Medium Specification Country/ Exposure limit Values
organization description
Food plant (specified) Brazil Acceptable limit (AL) 0.1-0.5 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) Germany Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.2-7.0 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) India Maximum tolerable concentration (MTC) 0.1-5.0 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) Russian Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1 mg/kg
Federation
Food cereals Sweden Maximum tolerable concentration (MTC) 0.1 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) United Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1-10.0 mg/kg
Kingdom
Food FAO Acceptable daily intake (ADI) 0.02 mg/kg body weight
Food plant (specified) FAO Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1-50 mg/kg
Air occupational Russian Maximum allowable concentration (MAC) 0.1 mg/m3
(aerosol) Federation
Water surface water Russian Maximum allowable concentration (MAC) 0.1 mg/litre
Federation
a From: IRPTC Legal File (1992).
The following label statements are required:
R40 - Possible risk of irreversible effects
S36/37 - Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves
Carbendazim has been classified as a Marine Pollutant and a
Flammable Solid by the International Maritime Organization.
7.5 Waste disposal
European Economic Community regulations require that carbendazim
and/or its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
FAO/WHO (1985a) Benomyl. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1983:
evaluations 1983. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 7-46.
FAO/WHO (1985b) Carbendazim. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1983:
evaluations 1983. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 89-121.
FAO/WHO (1988a) Benomyl. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1988:
evaluations 1988. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 5-15.
FAO/WHO (1988b) Carbendazim. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1988:
evaluations 1988. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 41-54.
ILO (1991) Occupational exposure limits for airborne toxic
substances. Geneva, International Labour Organisation
(Occupational Safety and Health Series, No. 37).
UNEP IRPTC (1992) IRPTC legal file 1992. Geneva, International
Register of Potentially Toxic Chemicals, United Nations Environment
Programme.
WHO (1993) Environmental Health Criteria 148: Benomyl. Geneva,
World Health Organization.
WHO (1993) Environmental Health Criteria 149: Carbendazim. Geneva,
World Health Organization.
 Common trade names
(including formulations): Carbendazim, Delsene, Bavistin,
Corbel, Konker, Bedazim, Derosal,
Kombat, Kemdazin, Carbendor, Hoe
017411, Cekudazim, Equitdazin,
Aimcozim (some are formulations with
other pesticides)
CAS chemical name: Methyl (1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate
Synonyms: Carbendazol (ZMAF), methyl-2-
benzimidazole carbamate (MBC, MCB,
BCM, BMC)
CAS registry number:
Common trade names
(including formulations): Carbendazim, Delsene, Bavistin,
Corbel, Konker, Bedazim, Derosal,
Kombat, Kemdazin, Carbendor, Hoe
017411, Cekudazim, Equitdazin,
Aimcozim (some are formulations with
other pesticides)
CAS chemical name: Methyl (1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate
Synonyms: Carbendazol (ZMAF), methyl-2-
benzimidazole carbamate (MBC, MCB,
BCM, BMC)
CAS registry number:  Table 1. Exposure limit values
Medium Specification Country/ Exposure limit Values
organization description
Food plant (specified) Brazil Acceptable limit (AL) 0.1-0.5 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) Germany Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.2-7.0 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) India Maximum tolerable concentration (MTC) 0.1-5.0 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) Russian Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1 mg/kg
Federation
Food cereals Sweden Maximum tolerable concentration (MTC) 0.1 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) United Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1-10.0 mg/kg
Kingdom
Food FAO Acceptable daily intake (ADI) 0.02 mg/kg body weight
Food plant (specified) FAO Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1-50 mg/kg
Air occupational Russian Maximum allowable concentration (MAC) 0.1 mg/m3
(aerosol) Federation
Water surface water Russian Maximum allowable concentration (MAC) 0.1 mg/litre
Federation
a From: IRPTC Legal File (1992).
The following label statements are required:
R40 - Possible risk of irreversible effects
S36/37 - Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves
Carbendazim has been classified as a Marine Pollutant and a
Flammable Solid by the International Maritime Organization.
7.5 Waste disposal
European Economic Community regulations require that carbendazim
and/or its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
FAO/WHO (1985a) Benomyl. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1983:
evaluations 1983. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 7-46.
FAO/WHO (1985b) Carbendazim. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1983:
evaluations 1983. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 89-121.
FAO/WHO (1988a) Benomyl. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1988:
evaluations 1988. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 5-15.
FAO/WHO (1988b) Carbendazim. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1988:
evaluations 1988. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 41-54.
ILO (1991) Occupational exposure limits for airborne toxic
substances. Geneva, International Labour Organisation
(Occupational Safety and Health Series, No. 37).
UNEP IRPTC (1992) IRPTC legal file 1992. Geneva, International
Register of Potentially Toxic Chemicals, United Nations Environment
Programme.
WHO (1993) Environmental Health Criteria 148: Benomyl. Geneva,
World Health Organization.
WHO (1993) Environmental Health Criteria 149: Carbendazim. Geneva,
World Health Organization.
Table 1. Exposure limit values
Medium Specification Country/ Exposure limit Values
organization description
Food plant (specified) Brazil Acceptable limit (AL) 0.1-0.5 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) Germany Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.2-7.0 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) India Maximum tolerable concentration (MTC) 0.1-5.0 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) Russian Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1 mg/kg
Federation
Food cereals Sweden Maximum tolerable concentration (MTC) 0.1 mg/kg
Food plant (specified) United Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1-10.0 mg/kg
Kingdom
Food FAO Acceptable daily intake (ADI) 0.02 mg/kg body weight
Food plant (specified) FAO Maximum residue limit (MRL) 0.1-50 mg/kg
Air occupational Russian Maximum allowable concentration (MAC) 0.1 mg/m3
(aerosol) Federation
Water surface water Russian Maximum allowable concentration (MAC) 0.1 mg/litre
Federation
a From: IRPTC Legal File (1992).
The following label statements are required:
R40 - Possible risk of irreversible effects
S36/37 - Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves
Carbendazim has been classified as a Marine Pollutant and a
Flammable Solid by the International Maritime Organization.
7.5 Waste disposal
European Economic Community regulations require that carbendazim
and/or its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
FAO/WHO (1985a) Benomyl. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1983:
evaluations 1983. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 7-46.
FAO/WHO (1985b) Carbendazim. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1983:
evaluations 1983. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 89-121.
FAO/WHO (1988a) Benomyl. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1988:
evaluations 1988. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 5-15.
FAO/WHO (1988b) Carbendazim. In: Pesticide residues in food - 1988:
evaluations 1988. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations, pp. 41-54.
ILO (1991) Occupational exposure limits for airborne toxic
substances. Geneva, International Labour Organisation
(Occupational Safety and Health Series, No. 37).
UNEP IRPTC (1992) IRPTC legal file 1992. Geneva, International
Register of Potentially Toxic Chemicals, United Nations Environment
Programme.
WHO (1993) Environmental Health Criteria 148: Benomyl. Geneva,
World Health Organization.
WHO (1993) Environmental Health Criteria 149: Carbendazim. Geneva,
World Health Organization.
