
TRIADIMENOL
EXPLANATION
Triadimenol has not been reviewed previously by JMPR. It is a
broad spectrum systemic fungicide consisting of a threo optical
isomer (isomer A) and an esythro isomer (isomer B). The ratio of
isomers was intially 60:40 and is now 80:20 due to a change in the
manufacturing process.
EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKE
BIOLOGICAL DATA
Biochemical aspects
Absorption, distribution and excretion
Rats
A study of the absorption, distribution and excretion of 14C
ring-labelled triadimenol (19.8 mCi/mM) was conducted in
Sprague-Dawley albino rats (Puhl & Hurley, 1978). Each of the two
diastereoisomers of triadimenol were individually examined in the
study of the pharmacokinetics. Two male and two females were given
a dose of 4 mg/kg bw by oral gavage. The 4 animals were housed in
glass metabolism cages and urine and feces were collected at 4, 8
(or at 6 hours for one of the isomers), 12, 24 hours and then daily
for 6 days. Expired gases were also collected and analysed.
Animals were sacrificed by decapitation and blood was collected.
Liver, kidney, heart, brain, muscle, fat and skin were collected and
analysed for radiolabel.
A half-life for excretion based on this study is estimated to
be approximately 24 hours for both males and females for isomer A
with 55% of radiolabel found in the feces for males and about 36%
for females. For isomer B, approximately 78% of the radiolabel was
found in the feces for males and about 44% was found in the feces of
females. Thus, slightly more radioactivity was excreted in the
feces by males with both isomers. About one-half of the radiolabel
was excreted in the urine by females with both of the isomers. No
radioactivity was found in the expired gas. Absorption and
distribution was rapid and excretion appeared to be first order.
Recovery ranged from 86.4 to 92.0%. Residues were less than
0.01 ppm, except in liver (0.01-0.06 ppm).
Biotransformation
In a study of metabolism and distribution, isomer A was
administered by oral gavage to 10 males and 10 females at a dose
level of 25 mg/kg bw. Two animals of each sex were sacrificed 1, 2,
4, 8 and 24 hours after dosing. Urine and feces were collected from
all animals at the time of sacrifice. Animals were sacrificed by
decapitation and blood, plasma and tissues (as noted above) were
collected. Radiolabel was counted and samples were extracted for
identification of specific metabolites.
Peak tissue levels were found after 4 hours in females and
after 1 hour in males. Levels fell rapidly after achieving peak
levels. The greatest amounts of radiolabel were found in the fat,
liver, skin and kidney with somewhat higher levels present in
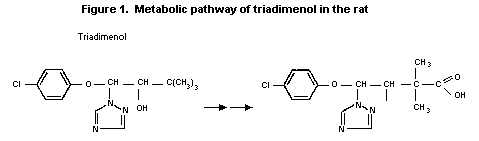
females at all intervals. The major metabolic pathway was found to
be hydroxylation of the t-butyl moiety and subsequent oxidation to
the carboxylic acid. Oxidation of the hydroxyl of the parent
compound also occurs to a minor extent. The metabolic pathway for
triadimenol is shown in Figure 1. The stereochemical orientation is
retained throughout metabolism and much more of isomer II is
excreted unchanged than isomer I. This selectivity of metabolic
enzymes for isomer I is more pronounced in males than females,
probably due to the greater microsomal activity present in rats.
 A dermal absorption study was conducted in Charles River Crl:CD
rats using 14C ring-labelled triadimenol (15.78 mCi/mM) (Leeling
et al. 1988). Twenty-four animals per dose level were dosed with
either .01, .1, 1 or 10 mg of test material on a 15 cm2 area of
shaved skin (equivalent to .04 to 40 mg/kg bw). Test material was
covered by a gauze patch after application. Four animals per dose
level were bled and then sacrificed at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8 and 24 hours
after dosing. Urine and feces were collected from each animal.
Radioactivity was also determined in whole carcass, skin wash and
excised skin. Dermal absorption was rapid. It was estimated that
50% of test material was likely to be absorbed and that absorption
was somewhat slower at higher concentrations (with half-lives for
elimination ranging from 27 hours at the low dose to 86 hours at the
high dose), suggesting a saturation of transport.
Toxicological studies
Acute toxicity
See Table 1.
In addition to the acute studies shown in the table above, skin
and eye irritation studies (Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b) and skin
sensitization studies (Flucke, 1981) were submitted for triadimenol.
All were considered to be "negative". Although no skin irritation
was observed in either man or the rabbit with 1, 2, 4-triazole, it
was found to be "strongly irritating" to the eye of the rabbit
(Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b).
Short-term studies
Rats
Groups of 10 albino Wistar II strain rats were exposed by
inhalation to triadimenol at concentrations averaging 0, 30.39
(26.8-31.8), 68.03 (61.2-73.0) and 229.71 (201-255) mg/m3 for 6
hours per day for 3 weeks (Kimmerle, 1976). Measurements were
gravimetric and concentrations reported are actual rather than
nominal. Control animals were exposed to only the
ethanol/polyethylene glycol solvent. No compound-related effect was
observed on any parameter examined. The NOAEL was 229.71 mg/m3.
TABLE 1. RESULTS OF ACUTE TOXICITY TESTING OF TRIADIMENOL AND METABOLITES
COMPOUND LD50
ADMINISTERED SEX SPECIES ROUTE (mg/kg bw) REFERENCE
Form A M Rat oral 579 Flucke, 1979a
Form B M Rat oral 5000 Flucke, 1979b
Forms A/B 60:40 M Rat oral 819 Flucke, 1979c
M Rat oral 897 Flucke, 1979c
Forms A/B 60:40 M Rat oral 1161 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
F Rat oral 1105 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M Rat i.p. 367 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
F Rat i.p. 352 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M&F dermal >5000 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M&F Rat inhalation >305 mg/m3 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
(4 hrs)
Forms A/B 80:20 M Rat oral 689 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat oral 752 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat oral 1098 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
F Rat oral 1037 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat i.p. 371 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
F Rat i.p. 286 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M&F Rat dermal >5000 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M&F Rat inhalation >1557 mg/m3 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
(1 hour)
TABLE 1 (contd.)
COMPOUND LD50
ADMINISTERED SEX SPECIES ROUTE (mg/kg bw) REFERENCE
Rat, inhalation M&F Rat inhalation >954 mg/m3 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
Metabolite M Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985a
KWG 1640 N F Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985a
Metabolite M Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985b
KWG 1342 N F Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985b
Metabolite M Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985c
KWG 1323 N F Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985c
1,2,4-triazole M Rat oral 1650 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
F Rat oral 1648 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
M Rat dermal 4200 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
F Rat dermal 3129 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
Two subchronic rat studies of 90 days duration have been
conducted. In the first, fifteen SPF Wistar rats per sex/dose were
fed diets containing either 150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol
technical (98% purity, A:B = 60:40) for 90 days (Löser & Kaliner,
1977). Thirty male and 30 female animals were fed control diet.
The rats were 28 to 32 days old at the start of the study.
One female rat in the mid-dose group died during the course of
the study. There was no compound-related effect on physical
appearance or behaviour or food consumption. Body weights of high
dose males and females were slightly but significantly depressed
during the course of the study. Several changes in hematology
parameters were significantly different at 2400 ppm: lower
hematocrit percent volume in females at one month, lower MCH and MCV
in males at 3 months, lower HCT in females at 3 months and a lower
hematrocrit percent volume in females at 3 months. Other hematology
and clinical chemistry and urinalysis findings were considered by
the authors to not be related to treatments. Absolute liver weights
of high dose males and females were elevated as were kidney and
ovary weights in high dose females. No histopathological changes
were considered to be related to test compound administration. The
NOAEL in this study was 600 ppm.
In the second 90 day rat study, Crj:CD rats obtained from
Charles River, Japan, were fed diets containing either 0, 120, 600
or 3000 ppm triadimenol technical (94% purity, A:B = 80:20) for 90
days (Nishimura & Nobuo, 1983). Twenty males and 20 females were
used at each dose level. Dose levels corresponded to 89.0, 39.6 and
208.5 mg/kg bw/day for males and 9.4, 46.4 and 221.1 mg/kg bw/day
based on food consumption measurements.
Piloerection and depilitation were observed at the high dose
level early in the study, no compound-related clinical observations
were noted in other groups or after the first month in the high dose
group. Body weight and food consumption were decreased only at the
high dose level. Urinalysis findings were unremarkable.
Significant decreases in hematocrit, hemoglobin and platelet counts
were noted in high dose males and females. Significantly lower
reticulocyte counts were noted in the mid and high dose groups of
both sexes. Because there were not corresponding histological
changes in the spleen and bone marrow, these findings were judged
not to be compound-related. Several parameters suggestive of
hepatotoxicity were affected at the highest dose level in this study
- eosinophilic degeneration of hepatocytes, fatty changes and
changes in triglycerides, free fatty acids, total cholesterol,
phospholipid, total protein, A/G ratio and albumin. The fatty
changes were observed primarily in the central to midzonal region in
male animals and in the peripheral region in female animals.
Increased absolute and relative liver weights were observed at both
the mid and high dose levels in both sexes. Several rats at both
dose levels had livers diagnosed as hypertrophic or as having a
"pronounced lobular pattern". Other changes in histology and in
other parameters were not considered to be compound-related. The
NOAEL was 120 ppm, equal to 8.0 for males and 9.4 for females for
this study.
In a comparison of the short-term toxicity of two ratios of
isomers, 20 SPF Wistar albino rats/sex/dose were given by oral
intubation either 0, 15, 45 or 100 mg/kg bw/day of 80:20 (A:B) or 45
or 100 mg/kg bw/day of 60:40 (A:B) for 4 weeks (Mihail & Vogel,
1981). One half of each group was sacrificed at the end of 4 weeks
and one half was observed for an additional 4-week recovery phase.
Liver enzymes (N- and O- demethylases and cytochrome P-450) were
determined at sacrifice.
All treated groups except those receiving 15 mg/kg bw/day
exhibited slightly increased CNS activity after administration of
test compound which lasted for approximately 2 hours after dosing.
The only other compound-related effects were on cytochrome P-450 and
N- and O-demethylase. Each of the induced enzymes returned to
control levels by the end of the recovery period. N-demethylase was
induced to a slightly greater extent by the 80:20 mixture,
cytochrome P-450 was slightly more induced by the 60:40 mixture.
There were no important toxicological differences between the
mixtures.
In a 4 week rat study, 20 male and 20 female Wistar II strain
albino rats were dosed by gavage with either 0, 1.5, 5, 15 or
45 mg/kg bw/day of technical material (98.5%) (Thyssen & Kaliner,
1976). One half of the animals in each group was kept under
observation for an additional 28 days before sacrifice.
No mortalities occurred and no compound-related behavioural
effects were noted. Body weights were similar in all groups. No
compound-related effects on clinical chemistry, hematology,
urinalysis, organ weight, gross or histopathology were observed.
Absolute and relative thyroid weights (male and female combined)
were significantly increased at 28 days but returned to normal at 56
days. The NOAEL was found to be 45 mg/kg bw/day (the highest dose
tested) in this study.
Rabbits
Groups of 6 New Zealand rabbits were exposed dermally for 6
hours to either 0, 50 or 250 mg/kg bw/day of test material (98%
purity) (Heimann & Schilde, 1984). Skin was clipped for all animals
and abraded for 3 animals per sex/dose prior to treatment. Material
was applied dissolved in distilled water with cremophor as an
emulsifier for 15 consecutive days. There were no indications of
topical or systemic effects which appeared to be compound-related.
The NOAEL was therefore 250 mg/kg bw/day.
Dogs
The first of three short-term toxicity studies in the dog was
conducted utilizing 4 male and 4 female beagle dogs per dose level
(Hoffmann & Kaliner, 1977). Dogs were fed diet containing either 0,
150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol technical (98.5% purity, A:B =
60:40) for 13 weeks. At the start of the study, the animals weighed
between 6.9 and 9.5 kg and were between 24 and 30 weeks old.
No mortalities were observed during the course of the study.
Occasional vomiting was observed after administration of the test
compound, no other clinical observations appeared to be
compound-related. There were no effects on reflexes, body
temperature, pulse or ophthalmology. There were no marked
differences between control animals and treated regarding water or
food intake. There was a slight depression of body weight gain in
both male and female groups at the high dose level compared to
control groups. Differences in hematological parameters between
groups did not appear to be compound-related. Several enzymatic
effects were as a consequence of test compound administration. GPT
levels were increased in a number of dogs in the mid and high dose
groups at the 6 and 13 week measurements. AP levels were generally
higher than controls in all treated groups both at the intermediate
and final measurements. Plasma cholesterol levels were also higher
in the mid and high dose groups both at the intermediate and final
measurements. Cytochrome P-450 and N-demethylase were elevated only
in the high dose group. Relative liver weights were increased in
both males and females at the high dose level. Absolute kidney
weights were also elevated in males at the high dose. No
histological changes were observed that were attributable to
treatment. The NOAEL was 600 ppm (equivalent to 45 mg/kg bw/day).
Purebred beagle dogs 32 to 36 weeks old and 7.5 to 12.5 kg in
weight, were randomized and divided in groups of 4 dogs/sex/dose
level and administered either 0, 150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol
technical (95% purity, A:B = 60:40) via the diet for 104 weeks
(Hoffmann & Vogel, 1984).
One female was sacrificed in moribund condition (in the high
dose group) during the course of the study but this was not
attributed to treatment. Clinical observations, tests of reflexes,
ophthalmoscopic observations, body weights and food intake were not
affected by treatment. However, body weights of all treated groups
were consistently lower than the control groups. This was
attributed to the unusually great body weight gain in both male and
female control groups. Hematological parameters that were examined
differed randomly and no effect of test compound was evident.
Elevated AP activity was noted in 4 high dose animals over the
course of the study. Slightly increased N-demethylase and
cytochrome P-450 were noted in the high dose group. Urinalysis
findings were similar in all groups. Organ weights were not affected
by treatment. No gross or histological findings were attributed to
treatment. A NOAEL cannot be established in this study due to an
apparent decrease in body weight gain in all treated groups.
A third feeding study in the dog was conducted using 6
animals/sex/dose (Hoffmann, 1984). The study was of 6 months'
duration and used dose levels of 90, 10, 30 and 100 ppm (purity
98.0%, A:B = 80:20). Parameters examined were identical to those in
the study discussed above with the exception of histology, for which
no examination took place. No effects were attributed to test
compound at the highest dose tested (equivalent to 7.5 mg/kg bw).
Long-term/carcinogenicity studies
Mice
Strain CF1/W 74 mice were administered triadimenol (A:B = 80%
premix) for 24 months in a combined oncogenicity/long-term toxicity
study (Bomhard & Löser, 1982). A total of 50 mice/sex/dose level
were fed diet containing either 0, 125, 500 or 2000 ppm of technical
triadimenol (95% purity) starting at 5 to 6 weeks of age. Animals
were examined daily, and were weighed weekly for the first 15 weeks
and every 3 weeks thereafter. Food consumption and concentration of
test compound was measured regularly. Clinical chemistry
measurements and hematological measurements were conducted at 0, 12
and 24 months. Gross pathological examination was conducted on all
animals dying or sacrificed. Heart, lungs, liver, spleen, kidney
and testicles were weighed. In addition to the weighed organs,
brain, pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, stomach, pancreas, urinary
bladder, ovaries and uterus, femur with skeletal muscle and nerve
were fixed, stained and examined histopathologically for all
animals.
Actual doses, based on food consumption measurements, were 30,
140 and 620 mg/kg bw/day for male mice and 50, 200 and 810 mg/kg
bw/day for female mice. Transient depressions of body weight gain
were observed in the low dose group. Consistent depression of body
weight gain was observed in males and females of both the mid and
high dose groups with the extent of depression somewhat greater in
male than in female mice. No group showed any apparent signs of
toxicity. Mortality was similar in all groups and ranged from 20 to
32% at 18 months and 62 to 78% at 24 months. Hematological
parameters did not appear to be affected by treatment.
Significantly elevated GOT was observed in male mice at the high
dose level and in female groups receiving test compound at 12
months. GPT was elevated and cholesterol depressed for the high
dose levels of both sexes at 12 months. SAP was elevated for mid-
and high dose male animals and total protein was depressed at the
interim measurement. At 24 months, GPT was slightly elevated in the
low dose and significantly elevated in the mid- and high dose levels
of both sexes. GOT was elevated in all treated groups, significantly
in low and high dose males and in mid- and high dose females. Other
clinical chemistry changes were not considered to be toxicologically
significant.
Organ weights were similar between groups with the exception of
liver weights, which were elevated in both sexes at the high dose
level. Females at the high dose level had a slightly increased
incidence of hyperplastic nodules (7 compared to 2 in the control
group) and there were more hyperplasias of the liver in high dose
males (5) than in the control group (2). No increase was observed
in total tumour incidence or the number of tumour-bearing animals.
A significantly higher incidence of liver adenomas was observed in
high dose females (6 adenomas compared to 0 adenomas and 1
adenocarcinoma in the control group). No liver tumours were noted
in the low dose and 4 adenomas and 1 adenocarcinoma were observed in
the mid dose group. This corresponds to an incidence of 2.3, 0,
10.4 and 12.3% for the 0, 125, 500 and 2000 ppm groups,
respectively. A higher incidence of thyroid cysts was noted in the
high dose males dying during the course of the study (5) than in
controls or in any other treated group (2 per group). Two
nonepithelial carcinosarcomas (a relatively rare tumour) were
observed in high dose males. The incidence of other neoplastic and
non-neoplastic findings were similar in all groups. Aspartate
aminotransferase (GOT) was elevated in all treated groups and the
increased incidence of liver tumours in mid and high dose females,
both of which appear to be compound-related. A NOAEL could not be
established for this study.
Rats
SPF rats of the strain BOR:WISW were administered test compound
(94.9% purity, A:B = 60:40) in the diet for 24 months at dose levels
of either 0, 125, 500 or 2000 ppm (Krötlinger et al. 1982). Each
dose level consisted of 60 males and 60 females. All animals were
observed daily. Body weights were recorded weekly until week 26;
afterwards, they were recorded every two weeks. Food consumption
was measured weekly. Urinalysis, hematology and clinical chemistry
measurements were conducted on 10 males and 10 females per dose
level at 3, 6, 12 and 24 months. All animals were examined grossly.
Thyroid, heart, lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys, adrenals, testes and
ovaries were weighed. In addition to the above tissues, the
following were examined microscopically for all animals: aorta,
eyes, intestine, femur, muscle, nerve, brain, urinary bladder,
pituitary, lymph nodes, stomach, spleen, epididymides, adrenals,
seminal vesicles, sternum, trachea and uterus. All grossly
remarkable tissues were examined histologically.
Survival during the course of the study was good with only 13%
to 30% mortality by the end of 24 months. Body weights of both
males and females at the high dose level were depressed during most
of the study compared to the respective control groups. Test
compound intake, taking into account food consumption, averaged 7,
25 and 105 mg/kg bw/day for males and 9, 35 and 144 mg/kg bw/day for
females. Although RBC counts were low for the high dose females and
males compared to the controls, the study authors noted that these
were within the physiologically normal range. Other hematological
parameters were similar in treated and control animals. GOT and GPT
were generally elevated in both males and females in the mid and
high dose levels during the course of the study. A slight elevation
in these parameters was observed in the low dose level animals
throughout the study which did not achieve statistical significance.
SAP was elevated only at the 12 month measurement in high dose
females. Other clinical chemistry parameters were not considered to
be affected by treatment. Both absolute and relative liver weights
were elevated in high dose females. Although both relative and
absolute ovarian weight was decreased in high dose females, these
and other organ weight changes (except for liver) were considered
random or the consequence of lower body weights in the high dose
group.
No gross pathological observations were noted that appeared to
be attributable to test compound. The most common tumour types were
pituitary and thyroid adenomas, adrenal pheochromocytomas, Leydig
cell tumours and uterine adenocarcinomas. No tumour type appeared
to be compound-related. The total number of tumours and the total
number of malignant tumours was similar in each group. No
non-neoplastic histopathological findings could be attributed to
treatment. The NOAEL was 125 ppm, equal to 7 mg/kg bw in males and
9 mg/kg bw in females.
Reproduction studies
Rats
A two-generation reproduction study was conducted in strain
BOR: WISW SPF rats (Löser & Eiben, 1984). Ten males and 20 females
were fed test compound (97.5% purity, A:B = 80:20) for 100 days
prior to the first mating at dose levels of 0, 20, 100 and 500 ppm.
Animals were weighed at weekly intervals before and after mating.
F0 animals were weighed at 3-day intervals during mating. F1b
females were weighed 1, 6, 15 and 20 days after insemination.
Animals were caged together for 5 days during mating and vaginal
smears were taken daily. The F1b litter was used to produce the
second generation. The F1a, F2a and F2b pups were lactated for 4
weeks after birth and sacrificed. Fertility, gestation, viability,
lactation and insemination indexes were calculated. Animals dying
during the course of the study and F2b pups and F1b parents were
grossly examined after sacrifice. The F1b parents had the
following organs weighed: liver, kidney, testicle and ovary.
Histopathological examination was conducted on tissues from the high
dose and control groups of F1b parents and 10 F2b male and 10 F2b
females.
Behaviour and mortality were not affected by treatment. Mean
group body weights were similar at all dose levels in the F0
generation but were depressed in the high dose level parental
animals of the F1b group and in F2a pups. Food consumption was also
slightly less for this group. There were no significant differences
between groups with regard to food intake. The fertility index,
mean litter size, lactation index, viability and insemination
indexes were not affected by treatment. The mean birth weight was
significantly decreased in the high dose pups F1b generation but no
effect on birth weight was observed in the first litter or in either
litter of the second generation. No apparent compound-related
toxicity was observed in any autopsied animals. There were no
histopathological changes which appeared to be related to treatment.
No toxicologically significant organ weight changes were found. The
No Observed Effect Level was 125 ppm (equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day).
Special studies on central nervous system effects
Mice
A study to investigate the central nervous system effects of
triadimenol was undertaken (Polacek, 1983). Test compound (98%
purity) was administered by a single gavage dose at levels of 0, 3
or 3.75, 15.0 and 60.0 mg/kg bw (except as noted below).
Hexobarbital sodium was administered to 10 mice per dose level 60
minutes after test compound. Mean time to anesthesia was
calculated. Examination of spontaneous motility was assessed by
administering test compound by gavage to 6 mice per dose level
(including dose levels of 1.0 and 4.0 mg/kg bw in addition to those
noted above) and recording motility every 5 minutes for 25 minutes.
Behaviour was assessed in mice by administering test compound
(including a dose level of 1.0 mg/kg bw) to 3 mice per dose to mice
which had been given glucose solution rather than food pellets the
previous night. Behavioural characteristics were assessed 30, 60
and 180 minutes after dosing. An "open field" test was conducted by
treating 10 mice with 2.5 mg amphetamine/kg bw 15 minutes after they
had received the test substance. Movement was quantitated after 30,
60 and 120 minutes. Finally, 5 mice were treated with reserpine
(5 mg/kg bw i.p.) and administered test compound 3 hours later.
Spontaneous activity and ptosis were assessed.
Triadimenol was found to potentiate hexabarbital anesthesia in
mice at all dose levels. Increased spontaneous motility was
observed with test compound alone at all dose levels except
1.9 mg/kg bw. Results were comparable between test compound and
caffeine with respect to increased motility at a given dose level.
Dose levels of 3.0 mg/kg bw was found to increase irritability and
12 mg/kg increased alertness, spontaneous activity and escape
response. The "open field-2 test found increased motor activity at
dose levels of 15 mg/kg bw and greater. The NOAEL was 3.75 mg/kg bw
for this test. Antagonism of reserpine was observed at doses of
12 mg/kg bw and greater.
Rats
As part of the study discussed above (Polacek, 1983), a "novel
box" behavioural test was conducted by dosing 10 rats with test
substance (at dose levels of 0, 3, 12 and 48 mg/kg bw) and observing
behaviour from 15 to 50 minutes. A dose of 48 mg/kg bw/day induced
CNS stimulation in the rat in the "novel box" test. The NOAEL was
12 mg/kg bw.
Special studies on metabolites
Short-term and teratology studies of the triadimenol metabolite
1,2,4-triazole are available (in addition to acute studies, see
above).
In the short-term study, 15 male and 15 female Wistar strain
rats received either 0, 100, 500 or 2500 ppm of 1,2,4-triazole in
the diet for 90 days (Bomhard et al. 1979). Lower body weights
and convulsions were observed in both sexes dosed at 2500 ppm.
Decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, MCV and MCH were observed in males
dosed at 2500 ppm at the study termination. Several high dose males
exhibited centro-lobular fat infiltration of the liver parenchyma
cells. The NOAEL was determined to be 500 ppm.
In the first teratology study, three groups of 25 Wistar rats
each received either 0, 100 or 200 mg/kg bw/day of 1,2,4-triazole by
oral gavage on days 6-15 of pregnancy (Renhof, 1988a). Body weight,
food consumption and behavioural signs were recorded for dams during
pregnancy. Fetuses were delivered on day 20 of gestation and were
examined for visceral, skeletal and external abnormalities.
The weight gain of dams dosed at 200 mg/kg bw was significantly
inhibited during and after dosing. At the 100 mg/kg bw dose level,
the incidence of fetuses with what were described as "slight bone
deviations" was increased, mean fetal weights were decreased and the
number of runts per litter was increased. An increase was found in
the number of pups with undescended testicles (11 pups from 7
litters compared to 2 pups from 2 litters in the control group). At
200 mg/kg bw, increases of resorptions and malformations were noted.
Malformations that appeared to be related to test compound included
hydronephrosis, cleft palate long bone dysplasia. Six fetuses were
noted to have undescended testicle in this group. A NOAEL was not
established in this study for embryo/ fetotoxicity. The NOAEL for
maternal toxicity was 100 mg/kg.
In a summary report for the second teratology study, it was
indicated that 25 Wistar rats per group received either 0, 10, 30 or
100 mg/kg bw/day by oral gavage on days 6 through 15 of gestation
(Renhof, 1988b). Parameters that were examined were identical to
the previous study.
Weight gain in the 100 mg/kg bw/day dams was less than other
groups. There was a decrease in fetal weight in this group and a
higher incidence of runts. There appeared to be no increase in
malformations or anomalies in any groups. The NOEL for maternal and
developmental toxicity was 30 mg/kg.
Special studies on mutagenicity
A variety of mutagenicity assays have been conducted with
triadimenol using both in vivo and in vitro systems. With the
exception of a Sister Chromatid Exchange assay which could not be
replicated, all assays were negative.
Special studies on teratology
Rat
In a summary report, no embryotoxicity or teratogenicity were
noted at dose levels of 10 or 30 mg/kg bw (A:B = 80:20, 95.2%
purity) administered by gavage to 25 strain BAY:FB 30 rats.
Maternal toxicity was reported at the highest dose level in the form
of decreased body weight gain (Renhof, 1984).
A range-finding study was conducted using Wistar/HAN rats
(Becker et al. 1986a). Five rats were dosed at either 0, 10, 50
or 150 g/kg bw/day on days 6 through 15 of gestation. Animals were
sacrificed on day 21. No maternal mortalities or signs and symptoms
of toxicity were reported. Body weight gain was clearly decreased
at the high dose level during and after treatment. Body weight gain
in other treated groups was similar to, or slightly greater than, in
control animals. A high rate of post-implantation loss (41.5%) was
observed at the high dose level. No external malformations were
observed in any group and fetal body weights were decreased only in
the high dose level compared to controls.
In the primary study, groups of Wistar/HAN rats were
administered technical triadimenol by gavage on days 6 through 15
post-coitum at dose levels of 0, 30, 60 and 120 mg/kg bw/day (Becker
et al. 1987a). Test material (purity 97.0%, A:B = 80:20) was
administered in distilled water with 0.5 cremophor EL as an
emulsifier. A total of 24, 25, 23 and 23 dams were utilized for the
0, 30, 60 and 120 mg/kg groups. Rats had been naturally mated until
a positive vaginal smear or a post-copulation plug was observed and
that day was designated as day 0 post-coitum. Body weights were
recorded daily, food consumption on days 6, 11, 16 and 21, and
clinical observations at least twice daily. All animals were
sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation on day 21 and the fetuses delivered
TABLE 2. MUTAGENICITY STUDIES ON TRIADIMENOL
CONCENTRATION
TEST SYSTEM TEST OBJECT OF TRIADIMENOL PURITY RESULTS REFERENCE
Lymphoma forward Mouse L5178Y cells 3.91-150 ug/ml 97.5% Negative Cifone, 1982
mutation assay (*)
Gene mutation (*) E. coli pol. A+, pol. A- 62.5-1000 ug/plate 97.5% Negative Herbold, 1981
Ames (*) S. typhimurium TA98, 4-2500 ug/plate 93.7% Negative Herbold, 1979b
TA100, TA1535, TA1537
Dominant lethal Mice 500 mg/kg 93.7% Negative Herbold, 1978a
Micronucleus Mice (NMRI bone marrow 2 x 350 mg/kg 93.7% Negativeq Herbold, 1978b
cells) 2 x 175 mg/kg
Micronucleus Mice (NMRI bone marrow 2 x 500 mg/kg 96.5% Negative Herbold, 1979a
cells) 2 x 350 mg/kg
Unscheduled DNA Rat hepatocytes .25-50 ug/ml 97.5% Negative Myhr, 1982
synthesis
Sister chromatid Chinese hamster ovary 38-225 ug/ml 93 Negative Putman, 1987
exchange cells
Sister chromatid Chinese hamster ovary 300 ug/ml 93 Equiv/Neg. Putman, 1982
exchange cells
Rec-assay Bacillus subtilis .05-10 mg/disk Negative Tanahashi & Miriya
NIG 45, 17 1982
(*) With and without metabolic activation.
by cesarian section. Gross pathological examination was conducted
on all dams, the uterine examined and corpora lutea and resorptions
were counted. All fetuses were weighed, sexed, and examined
grossly. One half of the fetuses were examined viscerally and the
remaining fetuses were cleared, stained and examined for skeletal
abnormalities.
No maternal deaths occurred during the course of the study.
The only clinical observation was a bloody vagina in one female of
the high dose group. No abnormal findings were noted in dams upon
necropsy. Mean body weights of treated groups were somewhat less
than the control groups at all times, including prior to dosing.
Body weights were significantly less at dose levels of 60 and
120 mg/kg than controls from day 7 (at 120 mg/kg) or day 8 (at
60 mg/kg) until day 18. Food consumption was significantly reduced
in all groups receiving test compound from day 6 to day 11. Reduced
food consumption continued to be evident in groups 3 and 4 until
study termination. Numbers of live fetuses, fetal weights, sex
ratios were similar at all dose levels. The number of embryonic
resorptions was increased at the high dose level (11.1% of total
implants compared to 5.9, 5.3 and 6.6% in the 0, 30 and 60 mg/kg
dose levels).
A variety of skeletal abnormalities were observed with an
elevated, but not dose-related, incidence in each treated group
compared to controls. A total of 5 fetuses (3.4%) from 4 litters
were affected in the control, 10 fetuses (6.6%) from 8 litters in
the low dose group, 16 fetuses (11.5%) from 12 litters in the
mid-dose group and 9 fetuses (6.7%) from 7 litters in the high dose.
Findings consisted primarily of abnormal ossification and
dumb-bell-shaped vertebrae. One case of hydrocephalus was observed
in both the control and low dose groups. One fetus evidenced
kyphosis and one multiple defects in the low dose group. No
malformations were observed in the mid or high dose groups. The
rate of skeletal malformations and/or anomalies was 0.99% in the
historical control population of 8492 (time period not specified).
The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 30 mg/kg bw based on reduced
food consumption and body weight gain at 60 and 120 mg/kg bw and
that the test compound did not reveal a teratogenic or embryotoxic
potential up to and including the highest dose tested.
In another rat teratology study, Long Evans FB 30 rats were
administered either 0, 10, 30 or 100 mg/kg bw (purity 93.7%, A:B =
60:40) by gavage on days 6 through 15 of gestation (Machemer, 1977).
Animals were naturally mated and the day that a positive vaginal
smear was found was considered to be day 0 of gestation. Twenty
animals at each dose level delivered litters for evaluation.
Animals were weighed during the treatment period and at the end of
gestation. Dams were examined at unspecified intervals. On day 20,
dams were sacrificed, the uterus examined and the fetuses and
litters were weighed. One-third of the fetuses at each dose level
were viscerally sectioned using the method of Wilson, two-thirds of
the fetuses were examined for skeletal abnormalities. All fetuses
were examined externally for malformations.
No compound-related effects on the appearance of the dams were
reported. No mortalities occurred. Weight gain was reported to be
significantly depressed during the treatment period although
individual data was not presented. A significant decrease in the
number of implantations was noted in the low dose group when
compared to controls, no effect was observed at other dose levels.
Four malformations in 3 litters were noted in the control group, 5
malformations in 2 litters in the low dose and 13 malformations in 3
litters was noted in the mid dose group. No malformations were
reported in the high dose group. Although data were not reported
for individual fetuses and neither group nor individual specific
variations were identified, the NOAEL for embryo/fetal toxicity
appeared to be 100 mg/kg bw and the NOAEL for maternal toxicity was
30 mg/kg bw based on decreased weight gain throughout gestation.
Rabbits
A range-finding study was conducted in Chinchilla hybrid
rabbits (Becker et al. 1986a). Dams were administered either 0,
50, 150 or 300 mg/kg bw of technical triadimenol (purity 97.0%, A:B
= 80:20) on days 6 through 18 post-coitum (3 per dose level for all
groups although only one rabbit at the high dose level delivered
live fetuses). One dam died at high dose level. Salivation,
dyspnea and abnormal posture were observed in dams at the high dose
level. Slight decreases in body weight gain and food consumption
were noted in the low and mid dose levels (although not
dose-related). Weight loss was noted at the high dose level. Total
post-implantation loss was noted in one of the two surviving dams at
the high dose. One malformed dead fetus was found upon external
examination of the uterine contents from a dam at the 150 mg/kg bw
dose level. Visceral and skeletal examinations were not conducted.
In the primary rabbit teratology study, groups of Chinchilla
hybrid rabbits were administered by daily gavage either 0, 8, 40 of
200 mg/kg bw triadimenol technical (97% purity, A:B = 80:20) in
water with 0.5% cremophor as an emulsifier on days 6 through 18
post-coitum (Becker et al. 1986b). Rabbits had been naturally
mated and the day mating was observed was recorded as day 0
post-coitum. A total of 16 pregnant rabbits served as the control
population and 15 rabbits in each of the remaining groups. All
animals were weighed daily, food consumption was measured on days 6,
11, 15, 19, 24 and 28. Clinical observations were recorded at least
twice daily. On day 28 of gestation, all rabbits were sacrificed
and fetuses delivered by Cesarean section. All fetuses were
examined externally, viscerally and cleared, stained and examined
for skeletal anomalies. Dams were subject to gross pathologic
examination, the uteri weighed and numbers of corpora lutea and
resorptions were recorded.
Maternal toxicity was observed at 200 mg/kg bw in the form of
CNS stimulation one-half hour to 6 hours after dosing, local areas
of hair loss, decreased food consumption and body weight gain.
There were no mortalities in any group. A marginal decrease in body
weight gain was observed at 40 mg/kg day. No other effects
attributed to test compound were noted at this dose level or at
8 mg/kg bw.
Post-implantation loss was elevated at 200 mg/kg bw with the
percentage of resorptions increasing from 3.8% per dam in the
control population to 12.8% in the 200 mg/kg bw group. Slight
reductions were observed in group mean body weight and litter mean
body weight in the high dose group. No malformations or anomalies
were observed in the control fetuses. A total of 3 fetuses from 3
litters, 2 fetuses from the same litter and 7 fetuses from 7 litters
were diagnosed with a variety of developmental abnormalities,
consisting primarily of ossification defects in the sternebrae and
vertebrae. The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 8 mg/kg bw/day
based on slightly decreased weight gain. A teratogenic potential
was not observed at dose levels as high as 200 mg/kg bw/day. The
NOAEL for fetotoxicity was 40 mg/kg bw based on increased
resorptions.
A teratology study had been previously conducted using New
Zealand rabbits (Korte & Osterburg, 1980). Groups of animals were
naturally mated and after a positive vaginal smear (considered as
gestation day 0), animals received HCG. On days 6 through 18 after
mating, 0, 10, 30 or 100 mg/kg bw (purity 97%, A:B = 80:20) was
administered by oral gavage in a water vehicle with cremophor EL as
an emulsifier. Although between 18 and 21 rabbits were inseminated
in each group, only 13, 10, 10 and 11 rabbits delivered live
offspring in the 0, 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg dose groups (2 animals in
the low dose and one each at the mid and high dose had complete
mortality of the litter). Two high dose animals died during the
course of the study with postmortem evidence of pneumonia. Body
weights were measured on days 0, 6, 18 and 28. After sacrifice,
gross autopsy was performed on each maternal animal. The number of
corpora lutea, implantations, live and dead fetuses were recorded.
All fetuses were examined for external, visceral and skeletal
abnormalities.
Body weight was slightly (but significantly) decreased in
females at the high dose level during the period of days 6-18. No
other indications of toxicity were observed in the dams. No
malformations of any type were observed in any of the fetuses. A
high incidence (ranging from 83 to 90%) of minor skeletal variations
were observed in each group. There was no apparent compound effect
on the incidence or pattern of these variations. The NOAEL for
maternal toxicity is 30 mg/kg bw in this study. The NOAEL for
fetotoxicity/ teratogenicity is 100 mg/kg bw.
Observations in humans
A statement was submitted which noted that "no adverse effects
on production workers engaged in the manufacture of the
(triadimenol) have been observed by us" (Kollert, 1981). Another
statement noted "no cases of health impairment were observed by us
with the periodically medically supervised employees (males and
females) which are involved in the formulation of BAYTAN applying
the usual safety measures" (Miksche, 1981).
COMMENTS
The two optical isomers of this chemical are both rapidly
absorbed and excreted, with slightly more of each isomer excreted in
urine by males than females. Hydroxylation of the tert-butyl
moiety and subsequent oxidation to carboxylic acid is the primary
route of metabolism. Although one of the two specific isomers is
about 10 times more acutely toxic than the other, no differences in
short-term toxicity were found in tests of the 80:20 and 60:40
mixtures of isomers in rats.
Triadimenol has a low acute toxicity in the species examined.
Several short-term studies have been conducted in rats. At
higher doses increased liver weights and liver hypertrophy were
observed. The NOAEL was 120 ppm, equal to 8 mg/kg bw/day.
Three short-term dog studies have been conducted. The NOAEL
was 100 ppm in the diet (equal to 7.5 mg/kg bw/day) based on
hepatotoxicity at the higher dose levels.
A long-term toxicity study was conducted in mice. An increased
incidence of hyperplastic nodules in the liver was observed in
females at 2000 ppm (equivalent to 300 mg/kg bw/day). There was an
increased incidence of liver tumours in females at the 500 and
2000 ppm levels (equivalent to 75 and 300 mg/kg bw/day). A NOAEL
could not be established for this study since aspartate
amino-transferase was elevated in all treated groups in a
dose-dependent manner.
No increases in any tumour type were observed in a long-term
feeding study in rats. Hepatotoxicity was observed at 500 ppm and
above. The NOAEL was 125 ppm (equal to 7 mg/kg bw/day).
In a 2-generation, 2 litters per generation reproduction study
in rats, the NOAEL was 125 ppm in the diet, equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day.
Decreased parental pup body weights were observed at a dose level of
500 ppm. Teratology studies were conducted in rats and rabbits. An
increased rate of resorption was found at the high dose in the rat
study (120 mg/kg bw/day) and rabbit study (200 mg/kg bw/day). The
NOAELs for embry-fetotoxicity were 60 mg/kg bw/day in the rat and
40 mg/kg bw/day in the rabbit.
After reviewing all available in vitro and in vivo
short-term tests, the meeting concluded that there was no evidence
of genotoxicity.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat: 125 ppm in the diet, equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day (based
on reproductive effects)
Dog: 100 ppm in the diet, equal to 7.5 mg/kg bw/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for humans
0-0.05 mg/kg bw.
Studies which will provide information in the continued evaluation
of the compound
Observations in humans.
REFERENCES
Becker, H., Frei, D. & Sachsse, K. (1986a) Dose-finding
embryotoxicity including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rabbit. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R 3692.
Becker, H., Frei, D. & Sachsse, K. (1986b) Dose-finding
embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rabbit. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Unpublished Report No. R 3826
submitted to WHO by Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Becker, H., Frei, D., Vogel, W. & Terrier, C. (1987a)
Embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rat. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R3988.
Becker, H., Mueller, E., Vogel, W. & Terrier, C. (1987b)
Embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rat. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R4145.
Bomhard, E. & Löser, E. (1982) KWG 0519 - Chronic toxicological
study on mice (feeding experiment over two years). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 10855.
Bomhard, E., Löser, E. & Schilde, B. (1979) 1,2,4-triazole.
Subchronic toxicological study with rats (feeding study over three
months). Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 8667.
Cifone, M.A. (1982) Mutagenicity evaluation of KWG 0519 in the
mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay. Litton Bionetics, Rockville,
Maryland. Report No. R 2204.
Flucke, W. (1981) KWG 0519 - Study of sensitization effect on
guinea pigs. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 9894.
Flucke, W. (1979a) KWG 0519 - Form A - Determination of acute
toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG.
Flucke, W. (1979b) KWG 0519 - Form B - Determination of acute
toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG.
Flucke, W. (1979c) KWG 0519 (Mixture of isomers) - Determination of
acute toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Heimann, K.G. (1985a) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13616.
Heimann, K.G. (1985b) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13617.
Heimann, K.G. (1985c) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13618.
Heimann, K.G. & Schilde, B. (1984) KWG 0519 - Subacute dermal
toxicity study on rabbits. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12496.
Herbold, B. (1981) KWG 0519 Triadimenol - The active ingredient of
Baytan. Study of DNA damage using the E. coli Pol-A1 test.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 102265.
Herbold, B. (1979a) KWG 0519 - Micronucleus test on mouse to
evaluate KWG 0519 for potential mutagenic effects. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 8584.
Herbold, B. (1979b) KWG 0519 - Salmonella/microsome test for
detection point -mutagenic effects. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer
AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 8189.
Herbold, B. (1978a) KWG 0519 - Dominant lethal study on male mouse
to test for mutagenic effects. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7900.
Herbold, B. (1978b) KWG 0519 - Micronucleus test on mouse to
evaluate KWG 0519 for potential mutagenic effects. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7588.
Hoffmann, K. & Vogel, O. (1984) KWG 0519 - First chronic study of
toxicity to dogs on oral administration (two-year feeding study).
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 12970.
Hoffmann, K. (1984) KWG 0519 - Second chronic study of toxicity to
dogs on oral administration (six-month feeding study). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12971.
Hoffmann, K. & Kaliner, G. (1977) KWG 0519 - Subchronic toxicity
study on dogs (thirteen-week feeding experiment). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6633.
Kimmerle, G. (1976) KWG 0519 - Subacute inhalation toxicity study
on rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 6321.
Kollert, W. (1981) BBA-requirement/effect on humans. Medical
Department EL, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Korte, R. & Osterburg, I. (1980) Embryotoxicity of KWG 0519 in
rabbits. Reprotox GmbH, Munster, FRG. Report No. R 1901.
Krötlinger, F., Löser, E. & Schilde, B. (1982) KWG 0519 - Chronic
toxicity study on rats (2-year feeding experiment). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 11009.
Leeling, J.L., Helms, R.J., Polomcak, S.C. & Craigo, L.A. (1988)
Dermal absorption of triadimenol-14C in rats. Miles, Inc.,
Elkhart, Indiana. Report No. Mobay 1055.
Löser, E. & Kaliner, G. (1977) KWG 0519 - Subchronic toxicity study
on rats (three-month feeding experiment). Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6811.
Löser , E. & Eibenm R. (1984) KWG 0519 - Two-generation study on
rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Report No. 12390.
Machemer, L. (1977) KWG 0519 - Evaluation for embryotoxic and
teratogenic effects on orally dosed rats. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7038.
Mihail, F. & Vogel, O. (1981) Study of comparative toxicity to rats
after 4-week administration using two test compound samples.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 9949.
Mihail, F. & Thyssen, J. (1980) KWG 0519 - Acute toxicity studies.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 9451.
Polacek, I. (1983) Central nervous effects of KWG 0519 (Pilot
study). Toxicological Institute, Bayer AG, Regenburg, FRG. Report
No. 2695.
Puhl, R.J. & Hurley, J.B. (1978) The metabolism and excretion of
Baytan by rats. Mobay Chemical Company, Stilwell, Kansas. Report
No. 66489 (FM 209).
Putman, D.L. (1987) Sister chromatid exchange assay in Chinese
hamster ovary (CHO) cells. Microbiological Associates, Rockville,
Maryland. Report No. 1022.
Renhof, M. (1984) KWG 0519 - Study for embryotoxic effects on rats
after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12687.
Renhof, M. (1988a) 1,2,4-triazole - Investigations into embryotoxic
effects on rats after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 17402.
Renhof, M. (1988b) 1,2,4-triazole - Investigations into embryotoxic
effects on rats after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 17401.
Tanahashi, N. & Moriya, M. (1982) Triadimenol - Microbial
mutagenicity study. Department of Toxicology, Institute of
Environmental Toxicology, Tokyo, Japan.
Thyssen, J. & Kaliner, G. (1976) KWG 0519 - Subacute oral
cumulative toxicity study on rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer
AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6481.
Thyssen, J. & Kimmerle, G. (1976a) KWG 0519 - Acute toxicity
studies. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer, AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 6090.
Thyssen, J. & Kimmerle, G. (1976b) 1,2,4-triazole. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer, AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 5926.
A dermal absorption study was conducted in Charles River Crl:CD
rats using 14C ring-labelled triadimenol (15.78 mCi/mM) (Leeling
et al. 1988). Twenty-four animals per dose level were dosed with
either .01, .1, 1 or 10 mg of test material on a 15 cm2 area of
shaved skin (equivalent to .04 to 40 mg/kg bw). Test material was
covered by a gauze patch after application. Four animals per dose
level were bled and then sacrificed at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8 and 24 hours
after dosing. Urine and feces were collected from each animal.
Radioactivity was also determined in whole carcass, skin wash and
excised skin. Dermal absorption was rapid. It was estimated that
50% of test material was likely to be absorbed and that absorption
was somewhat slower at higher concentrations (with half-lives for
elimination ranging from 27 hours at the low dose to 86 hours at the
high dose), suggesting a saturation of transport.
Toxicological studies
Acute toxicity
See Table 1.
In addition to the acute studies shown in the table above, skin
and eye irritation studies (Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b) and skin
sensitization studies (Flucke, 1981) were submitted for triadimenol.
All were considered to be "negative". Although no skin irritation
was observed in either man or the rabbit with 1, 2, 4-triazole, it
was found to be "strongly irritating" to the eye of the rabbit
(Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b).
Short-term studies
Rats
Groups of 10 albino Wistar II strain rats were exposed by
inhalation to triadimenol at concentrations averaging 0, 30.39
(26.8-31.8), 68.03 (61.2-73.0) and 229.71 (201-255) mg/m3 for 6
hours per day for 3 weeks (Kimmerle, 1976). Measurements were
gravimetric and concentrations reported are actual rather than
nominal. Control animals were exposed to only the
ethanol/polyethylene glycol solvent. No compound-related effect was
observed on any parameter examined. The NOAEL was 229.71 mg/m3.
TABLE 1. RESULTS OF ACUTE TOXICITY TESTING OF TRIADIMENOL AND METABOLITES
COMPOUND LD50
ADMINISTERED SEX SPECIES ROUTE (mg/kg bw) REFERENCE
Form A M Rat oral 579 Flucke, 1979a
Form B M Rat oral 5000 Flucke, 1979b
Forms A/B 60:40 M Rat oral 819 Flucke, 1979c
M Rat oral 897 Flucke, 1979c
Forms A/B 60:40 M Rat oral 1161 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
F Rat oral 1105 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M Rat i.p. 367 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
F Rat i.p. 352 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M&F dermal >5000 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M&F Rat inhalation >305 mg/m3 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
(4 hrs)
Forms A/B 80:20 M Rat oral 689 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat oral 752 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat oral 1098 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
F Rat oral 1037 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat i.p. 371 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
F Rat i.p. 286 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M&F Rat dermal >5000 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M&F Rat inhalation >1557 mg/m3 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
(1 hour)
TABLE 1 (contd.)
COMPOUND LD50
ADMINISTERED SEX SPECIES ROUTE (mg/kg bw) REFERENCE
Rat, inhalation M&F Rat inhalation >954 mg/m3 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
Metabolite M Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985a
KWG 1640 N F Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985a
Metabolite M Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985b
KWG 1342 N F Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985b
Metabolite M Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985c
KWG 1323 N F Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985c
1,2,4-triazole M Rat oral 1650 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
F Rat oral 1648 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
M Rat dermal 4200 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
F Rat dermal 3129 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
Two subchronic rat studies of 90 days duration have been
conducted. In the first, fifteen SPF Wistar rats per sex/dose were
fed diets containing either 150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol
technical (98% purity, A:B = 60:40) for 90 days (Löser & Kaliner,
1977). Thirty male and 30 female animals were fed control diet.
The rats were 28 to 32 days old at the start of the study.
One female rat in the mid-dose group died during the course of
the study. There was no compound-related effect on physical
appearance or behaviour or food consumption. Body weights of high
dose males and females were slightly but significantly depressed
during the course of the study. Several changes in hematology
parameters were significantly different at 2400 ppm: lower
hematocrit percent volume in females at one month, lower MCH and MCV
in males at 3 months, lower HCT in females at 3 months and a lower
hematrocrit percent volume in females at 3 months. Other hematology
and clinical chemistry and urinalysis findings were considered by
the authors to not be related to treatments. Absolute liver weights
of high dose males and females were elevated as were kidney and
ovary weights in high dose females. No histopathological changes
were considered to be related to test compound administration. The
NOAEL in this study was 600 ppm.
In the second 90 day rat study, Crj:CD rats obtained from
Charles River, Japan, were fed diets containing either 0, 120, 600
or 3000 ppm triadimenol technical (94% purity, A:B = 80:20) for 90
days (Nishimura & Nobuo, 1983). Twenty males and 20 females were
used at each dose level. Dose levels corresponded to 89.0, 39.6 and
208.5 mg/kg bw/day for males and 9.4, 46.4 and 221.1 mg/kg bw/day
based on food consumption measurements.
Piloerection and depilitation were observed at the high dose
level early in the study, no compound-related clinical observations
were noted in other groups or after the first month in the high dose
group. Body weight and food consumption were decreased only at the
high dose level. Urinalysis findings were unremarkable.
Significant decreases in hematocrit, hemoglobin and platelet counts
were noted in high dose males and females. Significantly lower
reticulocyte counts were noted in the mid and high dose groups of
both sexes. Because there were not corresponding histological
changes in the spleen and bone marrow, these findings were judged
not to be compound-related. Several parameters suggestive of
hepatotoxicity were affected at the highest dose level in this study
- eosinophilic degeneration of hepatocytes, fatty changes and
changes in triglycerides, free fatty acids, total cholesterol,
phospholipid, total protein, A/G ratio and albumin. The fatty
changes were observed primarily in the central to midzonal region in
male animals and in the peripheral region in female animals.
Increased absolute and relative liver weights were observed at both
the mid and high dose levels in both sexes. Several rats at both
dose levels had livers diagnosed as hypertrophic or as having a
"pronounced lobular pattern". Other changes in histology and in
other parameters were not considered to be compound-related. The
NOAEL was 120 ppm, equal to 8.0 for males and 9.4 for females for
this study.
In a comparison of the short-term toxicity of two ratios of
isomers, 20 SPF Wistar albino rats/sex/dose were given by oral
intubation either 0, 15, 45 or 100 mg/kg bw/day of 80:20 (A:B) or 45
or 100 mg/kg bw/day of 60:40 (A:B) for 4 weeks (Mihail & Vogel,
1981). One half of each group was sacrificed at the end of 4 weeks
and one half was observed for an additional 4-week recovery phase.
Liver enzymes (N- and O- demethylases and cytochrome P-450) were
determined at sacrifice.
All treated groups except those receiving 15 mg/kg bw/day
exhibited slightly increased CNS activity after administration of
test compound which lasted for approximately 2 hours after dosing.
The only other compound-related effects were on cytochrome P-450 and
N- and O-demethylase. Each of the induced enzymes returned to
control levels by the end of the recovery period. N-demethylase was
induced to a slightly greater extent by the 80:20 mixture,
cytochrome P-450 was slightly more induced by the 60:40 mixture.
There were no important toxicological differences between the
mixtures.
In a 4 week rat study, 20 male and 20 female Wistar II strain
albino rats were dosed by gavage with either 0, 1.5, 5, 15 or
45 mg/kg bw/day of technical material (98.5%) (Thyssen & Kaliner,
1976). One half of the animals in each group was kept under
observation for an additional 28 days before sacrifice.
No mortalities occurred and no compound-related behavioural
effects were noted. Body weights were similar in all groups. No
compound-related effects on clinical chemistry, hematology,
urinalysis, organ weight, gross or histopathology were observed.
Absolute and relative thyroid weights (male and female combined)
were significantly increased at 28 days but returned to normal at 56
days. The NOAEL was found to be 45 mg/kg bw/day (the highest dose
tested) in this study.
Rabbits
Groups of 6 New Zealand rabbits were exposed dermally for 6
hours to either 0, 50 or 250 mg/kg bw/day of test material (98%
purity) (Heimann & Schilde, 1984). Skin was clipped for all animals
and abraded for 3 animals per sex/dose prior to treatment. Material
was applied dissolved in distilled water with cremophor as an
emulsifier for 15 consecutive days. There were no indications of
topical or systemic effects which appeared to be compound-related.
The NOAEL was therefore 250 mg/kg bw/day.
Dogs
The first of three short-term toxicity studies in the dog was
conducted utilizing 4 male and 4 female beagle dogs per dose level
(Hoffmann & Kaliner, 1977). Dogs were fed diet containing either 0,
150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol technical (98.5% purity, A:B =
60:40) for 13 weeks. At the start of the study, the animals weighed
between 6.9 and 9.5 kg and were between 24 and 30 weeks old.
No mortalities were observed during the course of the study.
Occasional vomiting was observed after administration of the test
compound, no other clinical observations appeared to be
compound-related. There were no effects on reflexes, body
temperature, pulse or ophthalmology. There were no marked
differences between control animals and treated regarding water or
food intake. There was a slight depression of body weight gain in
both male and female groups at the high dose level compared to
control groups. Differences in hematological parameters between
groups did not appear to be compound-related. Several enzymatic
effects were as a consequence of test compound administration. GPT
levels were increased in a number of dogs in the mid and high dose
groups at the 6 and 13 week measurements. AP levels were generally
higher than controls in all treated groups both at the intermediate
and final measurements. Plasma cholesterol levels were also higher
in the mid and high dose groups both at the intermediate and final
measurements. Cytochrome P-450 and N-demethylase were elevated only
in the high dose group. Relative liver weights were increased in
both males and females at the high dose level. Absolute kidney
weights were also elevated in males at the high dose. No
histological changes were observed that were attributable to
treatment. The NOAEL was 600 ppm (equivalent to 45 mg/kg bw/day).
Purebred beagle dogs 32 to 36 weeks old and 7.5 to 12.5 kg in
weight, were randomized and divided in groups of 4 dogs/sex/dose
level and administered either 0, 150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol
technical (95% purity, A:B = 60:40) via the diet for 104 weeks
(Hoffmann & Vogel, 1984).
One female was sacrificed in moribund condition (in the high
dose group) during the course of the study but this was not
attributed to treatment. Clinical observations, tests of reflexes,
ophthalmoscopic observations, body weights and food intake were not
affected by treatment. However, body weights of all treated groups
were consistently lower than the control groups. This was
attributed to the unusually great body weight gain in both male and
female control groups. Hematological parameters that were examined
differed randomly and no effect of test compound was evident.
Elevated AP activity was noted in 4 high dose animals over the
course of the study. Slightly increased N-demethylase and
cytochrome P-450 were noted in the high dose group. Urinalysis
findings were similar in all groups. Organ weights were not affected
by treatment. No gross or histological findings were attributed to
treatment. A NOAEL cannot be established in this study due to an
apparent decrease in body weight gain in all treated groups.
A third feeding study in the dog was conducted using 6
animals/sex/dose (Hoffmann, 1984). The study was of 6 months'
duration and used dose levels of 90, 10, 30 and 100 ppm (purity
98.0%, A:B = 80:20). Parameters examined were identical to those in
the study discussed above with the exception of histology, for which
no examination took place. No effects were attributed to test
compound at the highest dose tested (equivalent to 7.5 mg/kg bw).
Long-term/carcinogenicity studies
Mice
Strain CF1/W 74 mice were administered triadimenol (A:B = 80%
premix) for 24 months in a combined oncogenicity/long-term toxicity
study (Bomhard & Löser, 1982). A total of 50 mice/sex/dose level
were fed diet containing either 0, 125, 500 or 2000 ppm of technical
triadimenol (95% purity) starting at 5 to 6 weeks of age. Animals
were examined daily, and were weighed weekly for the first 15 weeks
and every 3 weeks thereafter. Food consumption and concentration of
test compound was measured regularly. Clinical chemistry
measurements and hematological measurements were conducted at 0, 12
and 24 months. Gross pathological examination was conducted on all
animals dying or sacrificed. Heart, lungs, liver, spleen, kidney
and testicles were weighed. In addition to the weighed organs,
brain, pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, stomach, pancreas, urinary
bladder, ovaries and uterus, femur with skeletal muscle and nerve
were fixed, stained and examined histopathologically for all
animals.
Actual doses, based on food consumption measurements, were 30,
140 and 620 mg/kg bw/day for male mice and 50, 200 and 810 mg/kg
bw/day for female mice. Transient depressions of body weight gain
were observed in the low dose group. Consistent depression of body
weight gain was observed in males and females of both the mid and
high dose groups with the extent of depression somewhat greater in
male than in female mice. No group showed any apparent signs of
toxicity. Mortality was similar in all groups and ranged from 20 to
32% at 18 months and 62 to 78% at 24 months. Hematological
parameters did not appear to be affected by treatment.
Significantly elevated GOT was observed in male mice at the high
dose level and in female groups receiving test compound at 12
months. GPT was elevated and cholesterol depressed for the high
dose levels of both sexes at 12 months. SAP was elevated for mid-
and high dose male animals and total protein was depressed at the
interim measurement. At 24 months, GPT was slightly elevated in the
low dose and significantly elevated in the mid- and high dose levels
of both sexes. GOT was elevated in all treated groups, significantly
in low and high dose males and in mid- and high dose females. Other
clinical chemistry changes were not considered to be toxicologically
significant.
Organ weights were similar between groups with the exception of
liver weights, which were elevated in both sexes at the high dose
level. Females at the high dose level had a slightly increased
incidence of hyperplastic nodules (7 compared to 2 in the control
group) and there were more hyperplasias of the liver in high dose
males (5) than in the control group (2). No increase was observed
in total tumour incidence or the number of tumour-bearing animals.
A significantly higher incidence of liver adenomas was observed in
high dose females (6 adenomas compared to 0 adenomas and 1
adenocarcinoma in the control group). No liver tumours were noted
in the low dose and 4 adenomas and 1 adenocarcinoma were observed in
the mid dose group. This corresponds to an incidence of 2.3, 0,
10.4 and 12.3% for the 0, 125, 500 and 2000 ppm groups,
respectively. A higher incidence of thyroid cysts was noted in the
high dose males dying during the course of the study (5) than in
controls or in any other treated group (2 per group). Two
nonepithelial carcinosarcomas (a relatively rare tumour) were
observed in high dose males. The incidence of other neoplastic and
non-neoplastic findings were similar in all groups. Aspartate
aminotransferase (GOT) was elevated in all treated groups and the
increased incidence of liver tumours in mid and high dose females,
both of which appear to be compound-related. A NOAEL could not be
established for this study.
Rats
SPF rats of the strain BOR:WISW were administered test compound
(94.9% purity, A:B = 60:40) in the diet for 24 months at dose levels
of either 0, 125, 500 or 2000 ppm (Krötlinger et al. 1982). Each
dose level consisted of 60 males and 60 females. All animals were
observed daily. Body weights were recorded weekly until week 26;
afterwards, they were recorded every two weeks. Food consumption
was measured weekly. Urinalysis, hematology and clinical chemistry
measurements were conducted on 10 males and 10 females per dose
level at 3, 6, 12 and 24 months. All animals were examined grossly.
Thyroid, heart, lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys, adrenals, testes and
ovaries were weighed. In addition to the above tissues, the
following were examined microscopically for all animals: aorta,
eyes, intestine, femur, muscle, nerve, brain, urinary bladder,
pituitary, lymph nodes, stomach, spleen, epididymides, adrenals,
seminal vesicles, sternum, trachea and uterus. All grossly
remarkable tissues were examined histologically.
Survival during the course of the study was good with only 13%
to 30% mortality by the end of 24 months. Body weights of both
males and females at the high dose level were depressed during most
of the study compared to the respective control groups. Test
compound intake, taking into account food consumption, averaged 7,
25 and 105 mg/kg bw/day for males and 9, 35 and 144 mg/kg bw/day for
females. Although RBC counts were low for the high dose females and
males compared to the controls, the study authors noted that these
were within the physiologically normal range. Other hematological
parameters were similar in treated and control animals. GOT and GPT
were generally elevated in both males and females in the mid and
high dose levels during the course of the study. A slight elevation
in these parameters was observed in the low dose level animals
throughout the study which did not achieve statistical significance.
SAP was elevated only at the 12 month measurement in high dose
females. Other clinical chemistry parameters were not considered to
be affected by treatment. Both absolute and relative liver weights
were elevated in high dose females. Although both relative and
absolute ovarian weight was decreased in high dose females, these
and other organ weight changes (except for liver) were considered
random or the consequence of lower body weights in the high dose
group.
No gross pathological observations were noted that appeared to
be attributable to test compound. The most common tumour types were
pituitary and thyroid adenomas, adrenal pheochromocytomas, Leydig
cell tumours and uterine adenocarcinomas. No tumour type appeared
to be compound-related. The total number of tumours and the total
number of malignant tumours was similar in each group. No
non-neoplastic histopathological findings could be attributed to
treatment. The NOAEL was 125 ppm, equal to 7 mg/kg bw in males and
9 mg/kg bw in females.
Reproduction studies
Rats
A two-generation reproduction study was conducted in strain
BOR: WISW SPF rats (Löser & Eiben, 1984). Ten males and 20 females
were fed test compound (97.5% purity, A:B = 80:20) for 100 days
prior to the first mating at dose levels of 0, 20, 100 and 500 ppm.
Animals were weighed at weekly intervals before and after mating.
F0 animals were weighed at 3-day intervals during mating. F1b
females were weighed 1, 6, 15 and 20 days after insemination.
Animals were caged together for 5 days during mating and vaginal
smears were taken daily. The F1b litter was used to produce the
second generation. The F1a, F2a and F2b pups were lactated for 4
weeks after birth and sacrificed. Fertility, gestation, viability,
lactation and insemination indexes were calculated. Animals dying
during the course of the study and F2b pups and F1b parents were
grossly examined after sacrifice. The F1b parents had the
following organs weighed: liver, kidney, testicle and ovary.
Histopathological examination was conducted on tissues from the high
dose and control groups of F1b parents and 10 F2b male and 10 F2b
females.
Behaviour and mortality were not affected by treatment. Mean
group body weights were similar at all dose levels in the F0
generation but were depressed in the high dose level parental
animals of the F1b group and in F2a pups. Food consumption was also
slightly less for this group. There were no significant differences
between groups with regard to food intake. The fertility index,
mean litter size, lactation index, viability and insemination
indexes were not affected by treatment. The mean birth weight was
significantly decreased in the high dose pups F1b generation but no
effect on birth weight was observed in the first litter or in either
litter of the second generation. No apparent compound-related
toxicity was observed in any autopsied animals. There were no
histopathological changes which appeared to be related to treatment.
No toxicologically significant organ weight changes were found. The
No Observed Effect Level was 125 ppm (equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day).
Special studies on central nervous system effects
Mice
A study to investigate the central nervous system effects of
triadimenol was undertaken (Polacek, 1983). Test compound (98%
purity) was administered by a single gavage dose at levels of 0, 3
or 3.75, 15.0 and 60.0 mg/kg bw (except as noted below).
Hexobarbital sodium was administered to 10 mice per dose level 60
minutes after test compound. Mean time to anesthesia was
calculated. Examination of spontaneous motility was assessed by
administering test compound by gavage to 6 mice per dose level
(including dose levels of 1.0 and 4.0 mg/kg bw in addition to those
noted above) and recording motility every 5 minutes for 25 minutes.
Behaviour was assessed in mice by administering test compound
(including a dose level of 1.0 mg/kg bw) to 3 mice per dose to mice
which had been given glucose solution rather than food pellets the
previous night. Behavioural characteristics were assessed 30, 60
and 180 minutes after dosing. An "open field" test was conducted by
treating 10 mice with 2.5 mg amphetamine/kg bw 15 minutes after they
had received the test substance. Movement was quantitated after 30,
60 and 120 minutes. Finally, 5 mice were treated with reserpine
(5 mg/kg bw i.p.) and administered test compound 3 hours later.
Spontaneous activity and ptosis were assessed.
Triadimenol was found to potentiate hexabarbital anesthesia in
mice at all dose levels. Increased spontaneous motility was
observed with test compound alone at all dose levels except
1.9 mg/kg bw. Results were comparable between test compound and
caffeine with respect to increased motility at a given dose level.
Dose levels of 3.0 mg/kg bw was found to increase irritability and
12 mg/kg increased alertness, spontaneous activity and escape
response. The "open field-2 test found increased motor activity at
dose levels of 15 mg/kg bw and greater. The NOAEL was 3.75 mg/kg bw
for this test. Antagonism of reserpine was observed at doses of
12 mg/kg bw and greater.
Rats
As part of the study discussed above (Polacek, 1983), a "novel
box" behavioural test was conducted by dosing 10 rats with test
substance (at dose levels of 0, 3, 12 and 48 mg/kg bw) and observing
behaviour from 15 to 50 minutes. A dose of 48 mg/kg bw/day induced
CNS stimulation in the rat in the "novel box" test. The NOAEL was
12 mg/kg bw.
Special studies on metabolites
Short-term and teratology studies of the triadimenol metabolite
1,2,4-triazole are available (in addition to acute studies, see
above).
In the short-term study, 15 male and 15 female Wistar strain
rats received either 0, 100, 500 or 2500 ppm of 1,2,4-triazole in
the diet for 90 days (Bomhard et al. 1979). Lower body weights
and convulsions were observed in both sexes dosed at 2500 ppm.
Decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, MCV and MCH were observed in males
dosed at 2500 ppm at the study termination. Several high dose males
exhibited centro-lobular fat infiltration of the liver parenchyma
cells. The NOAEL was determined to be 500 ppm.
In the first teratology study, three groups of 25 Wistar rats
each received either 0, 100 or 200 mg/kg bw/day of 1,2,4-triazole by
oral gavage on days 6-15 of pregnancy (Renhof, 1988a). Body weight,
food consumption and behavioural signs were recorded for dams during
pregnancy. Fetuses were delivered on day 20 of gestation and were
examined for visceral, skeletal and external abnormalities.
The weight gain of dams dosed at 200 mg/kg bw was significantly
inhibited during and after dosing. At the 100 mg/kg bw dose level,
the incidence of fetuses with what were described as "slight bone
deviations" was increased, mean fetal weights were decreased and the
number of runts per litter was increased. An increase was found in
the number of pups with undescended testicles (11 pups from 7
litters compared to 2 pups from 2 litters in the control group). At
200 mg/kg bw, increases of resorptions and malformations were noted.
Malformations that appeared to be related to test compound included
hydronephrosis, cleft palate long bone dysplasia. Six fetuses were
noted to have undescended testicle in this group. A NOAEL was not
established in this study for embryo/ fetotoxicity. The NOAEL for
maternal toxicity was 100 mg/kg.
In a summary report for the second teratology study, it was
indicated that 25 Wistar rats per group received either 0, 10, 30 or
100 mg/kg bw/day by oral gavage on days 6 through 15 of gestation
(Renhof, 1988b). Parameters that were examined were identical to
the previous study.
Weight gain in the 100 mg/kg bw/day dams was less than other
groups. There was a decrease in fetal weight in this group and a
higher incidence of runts. There appeared to be no increase in
malformations or anomalies in any groups. The NOEL for maternal and
developmental toxicity was 30 mg/kg.
Special studies on mutagenicity
A variety of mutagenicity assays have been conducted with
triadimenol using both in vivo and in vitro systems. With the
exception of a Sister Chromatid Exchange assay which could not be
replicated, all assays were negative.
Special studies on teratology
Rat
In a summary report, no embryotoxicity or teratogenicity were
noted at dose levels of 10 or 30 mg/kg bw (A:B = 80:20, 95.2%
purity) administered by gavage to 25 strain BAY:FB 30 rats.
Maternal toxicity was reported at the highest dose level in the form
of decreased body weight gain (Renhof, 1984).
A range-finding study was conducted using Wistar/HAN rats
(Becker et al. 1986a). Five rats were dosed at either 0, 10, 50
or 150 g/kg bw/day on days 6 through 15 of gestation. Animals were
sacrificed on day 21. No maternal mortalities or signs and symptoms
of toxicity were reported. Body weight gain was clearly decreased
at the high dose level during and after treatment. Body weight gain
in other treated groups was similar to, or slightly greater than, in
control animals. A high rate of post-implantation loss (41.5%) was
observed at the high dose level. No external malformations were
observed in any group and fetal body weights were decreased only in
the high dose level compared to controls.
In the primary study, groups of Wistar/HAN rats were
administered technical triadimenol by gavage on days 6 through 15
post-coitum at dose levels of 0, 30, 60 and 120 mg/kg bw/day (Becker
et al. 1987a). Test material (purity 97.0%, A:B = 80:20) was
administered in distilled water with 0.5 cremophor EL as an
emulsifier. A total of 24, 25, 23 and 23 dams were utilized for the
0, 30, 60 and 120 mg/kg groups. Rats had been naturally mated until
a positive vaginal smear or a post-copulation plug was observed and
that day was designated as day 0 post-coitum. Body weights were
recorded daily, food consumption on days 6, 11, 16 and 21, and
clinical observations at least twice daily. All animals were
sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation on day 21 and the fetuses delivered
TABLE 2. MUTAGENICITY STUDIES ON TRIADIMENOL
CONCENTRATION
TEST SYSTEM TEST OBJECT OF TRIADIMENOL PURITY RESULTS REFERENCE
Lymphoma forward Mouse L5178Y cells 3.91-150 ug/ml 97.5% Negative Cifone, 1982
mutation assay (*)
Gene mutation (*) E. coli pol. A+, pol. A- 62.5-1000 ug/plate 97.5% Negative Herbold, 1981
Ames (*) S. typhimurium TA98, 4-2500 ug/plate 93.7% Negative Herbold, 1979b
TA100, TA1535, TA1537
Dominant lethal Mice 500 mg/kg 93.7% Negative Herbold, 1978a
Micronucleus Mice (NMRI bone marrow 2 x 350 mg/kg 93.7% Negativeq Herbold, 1978b
cells) 2 x 175 mg/kg
Micronucleus Mice (NMRI bone marrow 2 x 500 mg/kg 96.5% Negative Herbold, 1979a
cells) 2 x 350 mg/kg
Unscheduled DNA Rat hepatocytes .25-50 ug/ml 97.5% Negative Myhr, 1982
synthesis
Sister chromatid Chinese hamster ovary 38-225 ug/ml 93 Negative Putman, 1987
exchange cells
Sister chromatid Chinese hamster ovary 300 ug/ml 93 Equiv/Neg. Putman, 1982
exchange cells
Rec-assay Bacillus subtilis .05-10 mg/disk Negative Tanahashi & Miriya
NIG 45, 17 1982
(*) With and without metabolic activation.
by cesarian section. Gross pathological examination was conducted
on all dams, the uterine examined and corpora lutea and resorptions
were counted. All fetuses were weighed, sexed, and examined
grossly. One half of the fetuses were examined viscerally and the
remaining fetuses were cleared, stained and examined for skeletal
abnormalities.
No maternal deaths occurred during the course of the study.
The only clinical observation was a bloody vagina in one female of
the high dose group. No abnormal findings were noted in dams upon
necropsy. Mean body weights of treated groups were somewhat less
than the control groups at all times, including prior to dosing.
Body weights were significantly less at dose levels of 60 and
120 mg/kg than controls from day 7 (at 120 mg/kg) or day 8 (at
60 mg/kg) until day 18. Food consumption was significantly reduced
in all groups receiving test compound from day 6 to day 11. Reduced
food consumption continued to be evident in groups 3 and 4 until
study termination. Numbers of live fetuses, fetal weights, sex
ratios were similar at all dose levels. The number of embryonic
resorptions was increased at the high dose level (11.1% of total
implants compared to 5.9, 5.3 and 6.6% in the 0, 30 and 60 mg/kg
dose levels).
A variety of skeletal abnormalities were observed with an
elevated, but not dose-related, incidence in each treated group
compared to controls. A total of 5 fetuses (3.4%) from 4 litters
were affected in the control, 10 fetuses (6.6%) from 8 litters in
the low dose group, 16 fetuses (11.5%) from 12 litters in the
mid-dose group and 9 fetuses (6.7%) from 7 litters in the high dose.
Findings consisted primarily of abnormal ossification and
dumb-bell-shaped vertebrae. One case of hydrocephalus was observed
in both the control and low dose groups. One fetus evidenced
kyphosis and one multiple defects in the low dose group. No
malformations were observed in the mid or high dose groups. The
rate of skeletal malformations and/or anomalies was 0.99% in the
historical control population of 8492 (time period not specified).
The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 30 mg/kg bw based on reduced
food consumption and body weight gain at 60 and 120 mg/kg bw and
that the test compound did not reveal a teratogenic or embryotoxic
potential up to and including the highest dose tested.
In another rat teratology study, Long Evans FB 30 rats were
administered either 0, 10, 30 or 100 mg/kg bw (purity 93.7%, A:B =
60:40) by gavage on days 6 through 15 of gestation (Machemer, 1977).
Animals were naturally mated and the day that a positive vaginal
smear was found was considered to be day 0 of gestation. Twenty
animals at each dose level delivered litters for evaluation.
Animals were weighed during the treatment period and at the end of
gestation. Dams were examined at unspecified intervals. On day 20,
dams were sacrificed, the uterus examined and the fetuses and
litters were weighed. One-third of the fetuses at each dose level
were viscerally sectioned using the method of Wilson, two-thirds of
the fetuses were examined for skeletal abnormalities. All fetuses
were examined externally for malformations.
No compound-related effects on the appearance of the dams were
reported. No mortalities occurred. Weight gain was reported to be
significantly depressed during the treatment period although
individual data was not presented. A significant decrease in the
number of implantations was noted in the low dose group when
compared to controls, no effect was observed at other dose levels.
Four malformations in 3 litters were noted in the control group, 5
malformations in 2 litters in the low dose and 13 malformations in 3
litters was noted in the mid dose group. No malformations were
reported in the high dose group. Although data were not reported
for individual fetuses and neither group nor individual specific
variations were identified, the NOAEL for embryo/fetal toxicity
appeared to be 100 mg/kg bw and the NOAEL for maternal toxicity was
30 mg/kg bw based on decreased weight gain throughout gestation.
Rabbits
A range-finding study was conducted in Chinchilla hybrid
rabbits (Becker et al. 1986a). Dams were administered either 0,
50, 150 or 300 mg/kg bw of technical triadimenol (purity 97.0%, A:B
= 80:20) on days 6 through 18 post-coitum (3 per dose level for all
groups although only one rabbit at the high dose level delivered
live fetuses). One dam died at high dose level. Salivation,
dyspnea and abnormal posture were observed in dams at the high dose
level. Slight decreases in body weight gain and food consumption
were noted in the low and mid dose levels (although not
dose-related). Weight loss was noted at the high dose level. Total
post-implantation loss was noted in one of the two surviving dams at
the high dose. One malformed dead fetus was found upon external
examination of the uterine contents from a dam at the 150 mg/kg bw
dose level. Visceral and skeletal examinations were not conducted.
In the primary rabbit teratology study, groups of Chinchilla
hybrid rabbits were administered by daily gavage either 0, 8, 40 of
200 mg/kg bw triadimenol technical (97% purity, A:B = 80:20) in
water with 0.5% cremophor as an emulsifier on days 6 through 18
post-coitum (Becker et al. 1986b). Rabbits had been naturally
mated and the day mating was observed was recorded as day 0
post-coitum. A total of 16 pregnant rabbits served as the control
population and 15 rabbits in each of the remaining groups. All
animals were weighed daily, food consumption was measured on days 6,
11, 15, 19, 24 and 28. Clinical observations were recorded at least
twice daily. On day 28 of gestation, all rabbits were sacrificed
and fetuses delivered by Cesarean section. All fetuses were
examined externally, viscerally and cleared, stained and examined
for skeletal anomalies. Dams were subject to gross pathologic
examination, the uteri weighed and numbers of corpora lutea and
resorptions were recorded.
Maternal toxicity was observed at 200 mg/kg bw in the form of
CNS stimulation one-half hour to 6 hours after dosing, local areas
of hair loss, decreased food consumption and body weight gain.
There were no mortalities in any group. A marginal decrease in body
weight gain was observed at 40 mg/kg day. No other effects
attributed to test compound were noted at this dose level or at
8 mg/kg bw.
Post-implantation loss was elevated at 200 mg/kg bw with the
percentage of resorptions increasing from 3.8% per dam in the
control population to 12.8% in the 200 mg/kg bw group. Slight
reductions were observed in group mean body weight and litter mean
body weight in the high dose group. No malformations or anomalies
were observed in the control fetuses. A total of 3 fetuses from 3
litters, 2 fetuses from the same litter and 7 fetuses from 7 litters
were diagnosed with a variety of developmental abnormalities,
consisting primarily of ossification defects in the sternebrae and
vertebrae. The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 8 mg/kg bw/day
based on slightly decreased weight gain. A teratogenic potential
was not observed at dose levels as high as 200 mg/kg bw/day. The
NOAEL for fetotoxicity was 40 mg/kg bw based on increased
resorptions.
A teratology study had been previously conducted using New
Zealand rabbits (Korte & Osterburg, 1980). Groups of animals were
naturally mated and after a positive vaginal smear (considered as
gestation day 0), animals received HCG. On days 6 through 18 after
mating, 0, 10, 30 or 100 mg/kg bw (purity 97%, A:B = 80:20) was
administered by oral gavage in a water vehicle with cremophor EL as
an emulsifier. Although between 18 and 21 rabbits were inseminated
in each group, only 13, 10, 10 and 11 rabbits delivered live
offspring in the 0, 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg dose groups (2 animals in
the low dose and one each at the mid and high dose had complete
mortality of the litter). Two high dose animals died during the
course of the study with postmortem evidence of pneumonia. Body
weights were measured on days 0, 6, 18 and 28. After sacrifice,
gross autopsy was performed on each maternal animal. The number of
corpora lutea, implantations, live and dead fetuses were recorded.
All fetuses were examined for external, visceral and skeletal
abnormalities.
Body weight was slightly (but significantly) decreased in
females at the high dose level during the period of days 6-18. No
other indications of toxicity were observed in the dams. No
malformations of any type were observed in any of the fetuses. A
high incidence (ranging from 83 to 90%) of minor skeletal variations
were observed in each group. There was no apparent compound effect
on the incidence or pattern of these variations. The NOAEL for
maternal toxicity is 30 mg/kg bw in this study. The NOAEL for
fetotoxicity/ teratogenicity is 100 mg/kg bw.
Observations in humans
A statement was submitted which noted that "no adverse effects
on production workers engaged in the manufacture of the
(triadimenol) have been observed by us" (Kollert, 1981). Another
statement noted "no cases of health impairment were observed by us
with the periodically medically supervised employees (males and
females) which are involved in the formulation of BAYTAN applying
the usual safety measures" (Miksche, 1981).
COMMENTS
The two optical isomers of this chemical are both rapidly
absorbed and excreted, with slightly more of each isomer excreted in
urine by males than females. Hydroxylation of the tert-butyl
moiety and subsequent oxidation to carboxylic acid is the primary
route of metabolism. Although one of the two specific isomers is
about 10 times more acutely toxic than the other, no differences in
short-term toxicity were found in tests of the 80:20 and 60:40
mixtures of isomers in rats.
Triadimenol has a low acute toxicity in the species examined.
Several short-term studies have been conducted in rats. At
higher doses increased liver weights and liver hypertrophy were
observed. The NOAEL was 120 ppm, equal to 8 mg/kg bw/day.
Three short-term dog studies have been conducted. The NOAEL
was 100 ppm in the diet (equal to 7.5 mg/kg bw/day) based on
hepatotoxicity at the higher dose levels.
A long-term toxicity study was conducted in mice. An increased
incidence of hyperplastic nodules in the liver was observed in
females at 2000 ppm (equivalent to 300 mg/kg bw/day). There was an
increased incidence of liver tumours in females at the 500 and
2000 ppm levels (equivalent to 75 and 300 mg/kg bw/day). A NOAEL
could not be established for this study since aspartate
amino-transferase was elevated in all treated groups in a
dose-dependent manner.
No increases in any tumour type were observed in a long-term
feeding study in rats. Hepatotoxicity was observed at 500 ppm and
above. The NOAEL was 125 ppm (equal to 7 mg/kg bw/day).
In a 2-generation, 2 litters per generation reproduction study
in rats, the NOAEL was 125 ppm in the diet, equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day.
Decreased parental pup body weights were observed at a dose level of
500 ppm. Teratology studies were conducted in rats and rabbits. An
increased rate of resorption was found at the high dose in the rat
study (120 mg/kg bw/day) and rabbit study (200 mg/kg bw/day). The
NOAELs for embry-fetotoxicity were 60 mg/kg bw/day in the rat and
40 mg/kg bw/day in the rabbit.
After reviewing all available in vitro and in vivo
short-term tests, the meeting concluded that there was no evidence
of genotoxicity.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat: 125 ppm in the diet, equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day (based
on reproductive effects)
Dog: 100 ppm in the diet, equal to 7.5 mg/kg bw/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for humans
0-0.05 mg/kg bw.
Studies which will provide information in the continued evaluation
of the compound
Observations in humans.
REFERENCES
Becker, H., Frei, D. & Sachsse, K. (1986a) Dose-finding
embryotoxicity including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rabbit. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R 3692.
Becker, H., Frei, D. & Sachsse, K. (1986b) Dose-finding
embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rabbit. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Unpublished Report No. R 3826
submitted to WHO by Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Becker, H., Frei, D., Vogel, W. & Terrier, C. (1987a)
Embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rat. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R3988.
Becker, H., Mueller, E., Vogel, W. & Terrier, C. (1987b)
Embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rat. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R4145.
Bomhard, E. & Löser, E. (1982) KWG 0519 - Chronic toxicological
study on mice (feeding experiment over two years). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 10855.
Bomhard, E., Löser, E. & Schilde, B. (1979) 1,2,4-triazole.
Subchronic toxicological study with rats (feeding study over three
months). Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 8667.
Cifone, M.A. (1982) Mutagenicity evaluation of KWG 0519 in the
mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay. Litton Bionetics, Rockville,
Maryland. Report No. R 2204.
Flucke, W. (1981) KWG 0519 - Study of sensitization effect on
guinea pigs. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 9894.
Flucke, W. (1979a) KWG 0519 - Form A - Determination of acute
toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG.
Flucke, W. (1979b) KWG 0519 - Form B - Determination of acute
toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG.
Flucke, W. (1979c) KWG 0519 (Mixture of isomers) - Determination of
acute toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Heimann, K.G. (1985a) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13616.
Heimann, K.G. (1985b) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13617.
Heimann, K.G. (1985c) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13618.
Heimann, K.G. & Schilde, B. (1984) KWG 0519 - Subacute dermal
toxicity study on rabbits. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12496.
Herbold, B. (1981) KWG 0519 Triadimenol - The active ingredient of
Baytan. Study of DNA damage using the E. coli Pol-A1 test.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 102265.
Herbold, B. (1979a) KWG 0519 - Micronucleus test on mouse to
evaluate KWG 0519 for potential mutagenic effects. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 8584.
Herbold, B. (1979b) KWG 0519 - Salmonella/microsome test for
detection point -mutagenic effects. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer
AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 8189.
Herbold, B. (1978a) KWG 0519 - Dominant lethal study on male mouse
to test for mutagenic effects. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7900.
Herbold, B. (1978b) KWG 0519 - Micronucleus test on mouse to
evaluate KWG 0519 for potential mutagenic effects. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7588.
Hoffmann, K. & Vogel, O. (1984) KWG 0519 - First chronic study of
toxicity to dogs on oral administration (two-year feeding study).
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 12970.
Hoffmann, K. (1984) KWG 0519 - Second chronic study of toxicity to
dogs on oral administration (six-month feeding study). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12971.
Hoffmann, K. & Kaliner, G. (1977) KWG 0519 - Subchronic toxicity
study on dogs (thirteen-week feeding experiment). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6633.
Kimmerle, G. (1976) KWG 0519 - Subacute inhalation toxicity study
on rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 6321.
Kollert, W. (1981) BBA-requirement/effect on humans. Medical
Department EL, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Korte, R. & Osterburg, I. (1980) Embryotoxicity of KWG 0519 in
rabbits. Reprotox GmbH, Munster, FRG. Report No. R 1901.
Krötlinger, F., Löser, E. & Schilde, B. (1982) KWG 0519 - Chronic
toxicity study on rats (2-year feeding experiment). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 11009.
Leeling, J.L., Helms, R.J., Polomcak, S.C. & Craigo, L.A. (1988)
Dermal absorption of triadimenol-14C in rats. Miles, Inc.,
Elkhart, Indiana. Report No. Mobay 1055.
Löser, E. & Kaliner, G. (1977) KWG 0519 - Subchronic toxicity study
on rats (three-month feeding experiment). Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6811.
Löser , E. & Eibenm R. (1984) KWG 0519 - Two-generation study on
rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Report No. 12390.
Machemer, L. (1977) KWG 0519 - Evaluation for embryotoxic and
teratogenic effects on orally dosed rats. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7038.
Mihail, F. & Vogel, O. (1981) Study of comparative toxicity to rats
after 4-week administration using two test compound samples.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 9949.
Mihail, F. & Thyssen, J. (1980) KWG 0519 - Acute toxicity studies.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 9451.
Polacek, I. (1983) Central nervous effects of KWG 0519 (Pilot
study). Toxicological Institute, Bayer AG, Regenburg, FRG. Report
No. 2695.
Puhl, R.J. & Hurley, J.B. (1978) The metabolism and excretion of
Baytan by rats. Mobay Chemical Company, Stilwell, Kansas. Report
No. 66489 (FM 209).
Putman, D.L. (1987) Sister chromatid exchange assay in Chinese
hamster ovary (CHO) cells. Microbiological Associates, Rockville,
Maryland. Report No. 1022.
Renhof, M. (1984) KWG 0519 - Study for embryotoxic effects on rats
after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12687.
Renhof, M. (1988a) 1,2,4-triazole - Investigations into embryotoxic
effects on rats after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 17402.
Renhof, M. (1988b) 1,2,4-triazole - Investigations into embryotoxic
effects on rats after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 17401.
Tanahashi, N. & Moriya, M. (1982) Triadimenol - Microbial
mutagenicity study. Department of Toxicology, Institute of
Environmental Toxicology, Tokyo, Japan.
Thyssen, J. & Kaliner, G. (1976) KWG 0519 - Subacute oral
cumulative toxicity study on rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer
AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6481.
Thyssen, J. & Kimmerle, G. (1976a) KWG 0519 - Acute toxicity
studies. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer, AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 6090.
Thyssen, J. & Kimmerle, G. (1976b) 1,2,4-triazole. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer, AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 5926.
 A dermal absorption study was conducted in Charles River Crl:CD
rats using 14C ring-labelled triadimenol (15.78 mCi/mM) (Leeling
et al. 1988). Twenty-four animals per dose level were dosed with
either .01, .1, 1 or 10 mg of test material on a 15 cm2 area of
shaved skin (equivalent to .04 to 40 mg/kg bw). Test material was
covered by a gauze patch after application. Four animals per dose
level were bled and then sacrificed at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8 and 24 hours
after dosing. Urine and feces were collected from each animal.
Radioactivity was also determined in whole carcass, skin wash and
excised skin. Dermal absorption was rapid. It was estimated that
50% of test material was likely to be absorbed and that absorption
was somewhat slower at higher concentrations (with half-lives for
elimination ranging from 27 hours at the low dose to 86 hours at the
high dose), suggesting a saturation of transport.
Toxicological studies
Acute toxicity
See Table 1.
In addition to the acute studies shown in the table above, skin
and eye irritation studies (Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b) and skin
sensitization studies (Flucke, 1981) were submitted for triadimenol.
All were considered to be "negative". Although no skin irritation
was observed in either man or the rabbit with 1, 2, 4-triazole, it
was found to be "strongly irritating" to the eye of the rabbit
(Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b).
Short-term studies
Rats
Groups of 10 albino Wistar II strain rats were exposed by
inhalation to triadimenol at concentrations averaging 0, 30.39
(26.8-31.8), 68.03 (61.2-73.0) and 229.71 (201-255) mg/m3 for 6
hours per day for 3 weeks (Kimmerle, 1976). Measurements were
gravimetric and concentrations reported are actual rather than
nominal. Control animals were exposed to only the
ethanol/polyethylene glycol solvent. No compound-related effect was
observed on any parameter examined. The NOAEL was 229.71 mg/m3.
TABLE 1. RESULTS OF ACUTE TOXICITY TESTING OF TRIADIMENOL AND METABOLITES
COMPOUND LD50
ADMINISTERED SEX SPECIES ROUTE (mg/kg bw) REFERENCE
Form A M Rat oral 579 Flucke, 1979a
Form B M Rat oral 5000 Flucke, 1979b
Forms A/B 60:40 M Rat oral 819 Flucke, 1979c
M Rat oral 897 Flucke, 1979c
Forms A/B 60:40 M Rat oral 1161 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
F Rat oral 1105 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M Rat i.p. 367 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
F Rat i.p. 352 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M&F dermal >5000 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M&F Rat inhalation >305 mg/m3 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
(4 hrs)
Forms A/B 80:20 M Rat oral 689 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat oral 752 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat oral 1098 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
F Rat oral 1037 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat i.p. 371 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
F Rat i.p. 286 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M&F Rat dermal >5000 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M&F Rat inhalation >1557 mg/m3 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
(1 hour)
TABLE 1 (contd.)
COMPOUND LD50
ADMINISTERED SEX SPECIES ROUTE (mg/kg bw) REFERENCE
Rat, inhalation M&F Rat inhalation >954 mg/m3 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
Metabolite M Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985a
KWG 1640 N F Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985a
Metabolite M Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985b
KWG 1342 N F Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985b
Metabolite M Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985c
KWG 1323 N F Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985c
1,2,4-triazole M Rat oral 1650 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
F Rat oral 1648 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
M Rat dermal 4200 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
F Rat dermal 3129 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
Two subchronic rat studies of 90 days duration have been
conducted. In the first, fifteen SPF Wistar rats per sex/dose were
fed diets containing either 150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol
technical (98% purity, A:B = 60:40) for 90 days (Löser & Kaliner,
1977). Thirty male and 30 female animals were fed control diet.
The rats were 28 to 32 days old at the start of the study.
One female rat in the mid-dose group died during the course of
the study. There was no compound-related effect on physical
appearance or behaviour or food consumption. Body weights of high
dose males and females were slightly but significantly depressed
during the course of the study. Several changes in hematology
parameters were significantly different at 2400 ppm: lower
hematocrit percent volume in females at one month, lower MCH and MCV
in males at 3 months, lower HCT in females at 3 months and a lower
hematrocrit percent volume in females at 3 months. Other hematology
and clinical chemistry and urinalysis findings were considered by
the authors to not be related to treatments. Absolute liver weights
of high dose males and females were elevated as were kidney and
ovary weights in high dose females. No histopathological changes
were considered to be related to test compound administration. The
NOAEL in this study was 600 ppm.
In the second 90 day rat study, Crj:CD rats obtained from
Charles River, Japan, were fed diets containing either 0, 120, 600
or 3000 ppm triadimenol technical (94% purity, A:B = 80:20) for 90
days (Nishimura & Nobuo, 1983). Twenty males and 20 females were
used at each dose level. Dose levels corresponded to 89.0, 39.6 and
208.5 mg/kg bw/day for males and 9.4, 46.4 and 221.1 mg/kg bw/day
based on food consumption measurements.
Piloerection and depilitation were observed at the high dose
level early in the study, no compound-related clinical observations
were noted in other groups or after the first month in the high dose
group. Body weight and food consumption were decreased only at the
high dose level. Urinalysis findings were unremarkable.
Significant decreases in hematocrit, hemoglobin and platelet counts
were noted in high dose males and females. Significantly lower
reticulocyte counts were noted in the mid and high dose groups of
both sexes. Because there were not corresponding histological
changes in the spleen and bone marrow, these findings were judged
not to be compound-related. Several parameters suggestive of
hepatotoxicity were affected at the highest dose level in this study
- eosinophilic degeneration of hepatocytes, fatty changes and
changes in triglycerides, free fatty acids, total cholesterol,
phospholipid, total protein, A/G ratio and albumin. The fatty
changes were observed primarily in the central to midzonal region in
male animals and in the peripheral region in female animals.
Increased absolute and relative liver weights were observed at both
the mid and high dose levels in both sexes. Several rats at both
dose levels had livers diagnosed as hypertrophic or as having a
"pronounced lobular pattern". Other changes in histology and in
other parameters were not considered to be compound-related. The
NOAEL was 120 ppm, equal to 8.0 for males and 9.4 for females for
this study.
In a comparison of the short-term toxicity of two ratios of
isomers, 20 SPF Wistar albino rats/sex/dose were given by oral
intubation either 0, 15, 45 or 100 mg/kg bw/day of 80:20 (A:B) or 45
or 100 mg/kg bw/day of 60:40 (A:B) for 4 weeks (Mihail & Vogel,
1981). One half of each group was sacrificed at the end of 4 weeks
and one half was observed for an additional 4-week recovery phase.
Liver enzymes (N- and O- demethylases and cytochrome P-450) were
determined at sacrifice.
All treated groups except those receiving 15 mg/kg bw/day
exhibited slightly increased CNS activity after administration of
test compound which lasted for approximately 2 hours after dosing.
The only other compound-related effects were on cytochrome P-450 and
N- and O-demethylase. Each of the induced enzymes returned to
control levels by the end of the recovery period. N-demethylase was
induced to a slightly greater extent by the 80:20 mixture,
cytochrome P-450 was slightly more induced by the 60:40 mixture.
There were no important toxicological differences between the
mixtures.
In a 4 week rat study, 20 male and 20 female Wistar II strain
albino rats were dosed by gavage with either 0, 1.5, 5, 15 or
45 mg/kg bw/day of technical material (98.5%) (Thyssen & Kaliner,
1976). One half of the animals in each group was kept under
observation for an additional 28 days before sacrifice.
No mortalities occurred and no compound-related behavioural
effects were noted. Body weights were similar in all groups. No
compound-related effects on clinical chemistry, hematology,
urinalysis, organ weight, gross or histopathology were observed.
Absolute and relative thyroid weights (male and female combined)
were significantly increased at 28 days but returned to normal at 56
days. The NOAEL was found to be 45 mg/kg bw/day (the highest dose
tested) in this study.
Rabbits
Groups of 6 New Zealand rabbits were exposed dermally for 6
hours to either 0, 50 or 250 mg/kg bw/day of test material (98%
purity) (Heimann & Schilde, 1984). Skin was clipped for all animals
and abraded for 3 animals per sex/dose prior to treatment. Material
was applied dissolved in distilled water with cremophor as an
emulsifier for 15 consecutive days. There were no indications of
topical or systemic effects which appeared to be compound-related.
The NOAEL was therefore 250 mg/kg bw/day.
Dogs
The first of three short-term toxicity studies in the dog was
conducted utilizing 4 male and 4 female beagle dogs per dose level
(Hoffmann & Kaliner, 1977). Dogs were fed diet containing either 0,
150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol technical (98.5% purity, A:B =
60:40) for 13 weeks. At the start of the study, the animals weighed
between 6.9 and 9.5 kg and were between 24 and 30 weeks old.
No mortalities were observed during the course of the study.
Occasional vomiting was observed after administration of the test
compound, no other clinical observations appeared to be
compound-related. There were no effects on reflexes, body
temperature, pulse or ophthalmology. There were no marked
differences between control animals and treated regarding water or
food intake. There was a slight depression of body weight gain in
both male and female groups at the high dose level compared to
control groups. Differences in hematological parameters between
groups did not appear to be compound-related. Several enzymatic
effects were as a consequence of test compound administration. GPT
levels were increased in a number of dogs in the mid and high dose
groups at the 6 and 13 week measurements. AP levels were generally
higher than controls in all treated groups both at the intermediate
and final measurements. Plasma cholesterol levels were also higher
in the mid and high dose groups both at the intermediate and final
measurements. Cytochrome P-450 and N-demethylase were elevated only
in the high dose group. Relative liver weights were increased in
both males and females at the high dose level. Absolute kidney
weights were also elevated in males at the high dose. No
histological changes were observed that were attributable to
treatment. The NOAEL was 600 ppm (equivalent to 45 mg/kg bw/day).
Purebred beagle dogs 32 to 36 weeks old and 7.5 to 12.5 kg in
weight, were randomized and divided in groups of 4 dogs/sex/dose
level and administered either 0, 150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol
technical (95% purity, A:B = 60:40) via the diet for 104 weeks
(Hoffmann & Vogel, 1984).
One female was sacrificed in moribund condition (in the high
dose group) during the course of the study but this was not
attributed to treatment. Clinical observations, tests of reflexes,
ophthalmoscopic observations, body weights and food intake were not
affected by treatment. However, body weights of all treated groups
were consistently lower than the control groups. This was
attributed to the unusually great body weight gain in both male and
female control groups. Hematological parameters that were examined
differed randomly and no effect of test compound was evident.
Elevated AP activity was noted in 4 high dose animals over the
course of the study. Slightly increased N-demethylase and
cytochrome P-450 were noted in the high dose group. Urinalysis
findings were similar in all groups. Organ weights were not affected
by treatment. No gross or histological findings were attributed to
treatment. A NOAEL cannot be established in this study due to an
apparent decrease in body weight gain in all treated groups.
A third feeding study in the dog was conducted using 6
animals/sex/dose (Hoffmann, 1984). The study was of 6 months'
duration and used dose levels of 90, 10, 30 and 100 ppm (purity
98.0%, A:B = 80:20). Parameters examined were identical to those in
the study discussed above with the exception of histology, for which
no examination took place. No effects were attributed to test
compound at the highest dose tested (equivalent to 7.5 mg/kg bw).
Long-term/carcinogenicity studies
Mice
Strain CF1/W 74 mice were administered triadimenol (A:B = 80%
premix) for 24 months in a combined oncogenicity/long-term toxicity
study (Bomhard & Löser, 1982). A total of 50 mice/sex/dose level
were fed diet containing either 0, 125, 500 or 2000 ppm of technical
triadimenol (95% purity) starting at 5 to 6 weeks of age. Animals
were examined daily, and were weighed weekly for the first 15 weeks
and every 3 weeks thereafter. Food consumption and concentration of
test compound was measured regularly. Clinical chemistry
measurements and hematological measurements were conducted at 0, 12
and 24 months. Gross pathological examination was conducted on all
animals dying or sacrificed. Heart, lungs, liver, spleen, kidney
and testicles were weighed. In addition to the weighed organs,
brain, pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, stomach, pancreas, urinary
bladder, ovaries and uterus, femur with skeletal muscle and nerve
were fixed, stained and examined histopathologically for all
animals.
Actual doses, based on food consumption measurements, were 30,
140 and 620 mg/kg bw/day for male mice and 50, 200 and 810 mg/kg
bw/day for female mice. Transient depressions of body weight gain
were observed in the low dose group. Consistent depression of body
weight gain was observed in males and females of both the mid and
high dose groups with the extent of depression somewhat greater in
male than in female mice. No group showed any apparent signs of
toxicity. Mortality was similar in all groups and ranged from 20 to
32% at 18 months and 62 to 78% at 24 months. Hematological
parameters did not appear to be affected by treatment.
Significantly elevated GOT was observed in male mice at the high
dose level and in female groups receiving test compound at 12
months. GPT was elevated and cholesterol depressed for the high
dose levels of both sexes at 12 months. SAP was elevated for mid-
and high dose male animals and total protein was depressed at the
interim measurement. At 24 months, GPT was slightly elevated in the
low dose and significantly elevated in the mid- and high dose levels
of both sexes. GOT was elevated in all treated groups, significantly
in low and high dose males and in mid- and high dose females. Other
clinical chemistry changes were not considered to be toxicologically
significant.
Organ weights were similar between groups with the exception of
liver weights, which were elevated in both sexes at the high dose
level. Females at the high dose level had a slightly increased
incidence of hyperplastic nodules (7 compared to 2 in the control
group) and there were more hyperplasias of the liver in high dose
males (5) than in the control group (2). No increase was observed
in total tumour incidence or the number of tumour-bearing animals.
A significantly higher incidence of liver adenomas was observed in
high dose females (6 adenomas compared to 0 adenomas and 1
adenocarcinoma in the control group). No liver tumours were noted
in the low dose and 4 adenomas and 1 adenocarcinoma were observed in
the mid dose group. This corresponds to an incidence of 2.3, 0,
10.4 and 12.3% for the 0, 125, 500 and 2000 ppm groups,
respectively. A higher incidence of thyroid cysts was noted in the
high dose males dying during the course of the study (5) than in
controls or in any other treated group (2 per group). Two
nonepithelial carcinosarcomas (a relatively rare tumour) were
observed in high dose males. The incidence of other neoplastic and
non-neoplastic findings were similar in all groups. Aspartate
aminotransferase (GOT) was elevated in all treated groups and the
increased incidence of liver tumours in mid and high dose females,
both of which appear to be compound-related. A NOAEL could not be
established for this study.
Rats
SPF rats of the strain BOR:WISW were administered test compound
(94.9% purity, A:B = 60:40) in the diet for 24 months at dose levels
of either 0, 125, 500 or 2000 ppm (Krötlinger et al. 1982). Each
dose level consisted of 60 males and 60 females. All animals were
observed daily. Body weights were recorded weekly until week 26;
afterwards, they were recorded every two weeks. Food consumption
was measured weekly. Urinalysis, hematology and clinical chemistry
measurements were conducted on 10 males and 10 females per dose
level at 3, 6, 12 and 24 months. All animals were examined grossly.
Thyroid, heart, lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys, adrenals, testes and
ovaries were weighed. In addition to the above tissues, the
following were examined microscopically for all animals: aorta,
eyes, intestine, femur, muscle, nerve, brain, urinary bladder,
pituitary, lymph nodes, stomach, spleen, epididymides, adrenals,
seminal vesicles, sternum, trachea and uterus. All grossly
remarkable tissues were examined histologically.
Survival during the course of the study was good with only 13%
to 30% mortality by the end of 24 months. Body weights of both
males and females at the high dose level were depressed during most
of the study compared to the respective control groups. Test
compound intake, taking into account food consumption, averaged 7,
25 and 105 mg/kg bw/day for males and 9, 35 and 144 mg/kg bw/day for
females. Although RBC counts were low for the high dose females and
males compared to the controls, the study authors noted that these
were within the physiologically normal range. Other hematological
parameters were similar in treated and control animals. GOT and GPT
were generally elevated in both males and females in the mid and
high dose levels during the course of the study. A slight elevation
in these parameters was observed in the low dose level animals
throughout the study which did not achieve statistical significance.
SAP was elevated only at the 12 month measurement in high dose
females. Other clinical chemistry parameters were not considered to
be affected by treatment. Both absolute and relative liver weights
were elevated in high dose females. Although both relative and
absolute ovarian weight was decreased in high dose females, these
and other organ weight changes (except for liver) were considered
random or the consequence of lower body weights in the high dose
group.
No gross pathological observations were noted that appeared to
be attributable to test compound. The most common tumour types were
pituitary and thyroid adenomas, adrenal pheochromocytomas, Leydig
cell tumours and uterine adenocarcinomas. No tumour type appeared
to be compound-related. The total number of tumours and the total
number of malignant tumours was similar in each group. No
non-neoplastic histopathological findings could be attributed to
treatment. The NOAEL was 125 ppm, equal to 7 mg/kg bw in males and
9 mg/kg bw in females.
Reproduction studies
Rats
A two-generation reproduction study was conducted in strain
BOR: WISW SPF rats (Löser & Eiben, 1984). Ten males and 20 females
were fed test compound (97.5% purity, A:B = 80:20) for 100 days
prior to the first mating at dose levels of 0, 20, 100 and 500 ppm.
Animals were weighed at weekly intervals before and after mating.
F0 animals were weighed at 3-day intervals during mating. F1b
females were weighed 1, 6, 15 and 20 days after insemination.
Animals were caged together for 5 days during mating and vaginal
smears were taken daily. The F1b litter was used to produce the
second generation. The F1a, F2a and F2b pups were lactated for 4
weeks after birth and sacrificed. Fertility, gestation, viability,
lactation and insemination indexes were calculated. Animals dying
during the course of the study and F2b pups and F1b parents were
grossly examined after sacrifice. The F1b parents had the
following organs weighed: liver, kidney, testicle and ovary.
Histopathological examination was conducted on tissues from the high
dose and control groups of F1b parents and 10 F2b male and 10 F2b
females.
Behaviour and mortality were not affected by treatment. Mean
group body weights were similar at all dose levels in the F0
generation but were depressed in the high dose level parental
animals of the F1b group and in F2a pups. Food consumption was also
slightly less for this group. There were no significant differences
between groups with regard to food intake. The fertility index,
mean litter size, lactation index, viability and insemination
indexes were not affected by treatment. The mean birth weight was
significantly decreased in the high dose pups F1b generation but no
effect on birth weight was observed in the first litter or in either
litter of the second generation. No apparent compound-related
toxicity was observed in any autopsied animals. There were no
histopathological changes which appeared to be related to treatment.
No toxicologically significant organ weight changes were found. The
No Observed Effect Level was 125 ppm (equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day).
Special studies on central nervous system effects
Mice
A study to investigate the central nervous system effects of
triadimenol was undertaken (Polacek, 1983). Test compound (98%
purity) was administered by a single gavage dose at levels of 0, 3
or 3.75, 15.0 and 60.0 mg/kg bw (except as noted below).
Hexobarbital sodium was administered to 10 mice per dose level 60
minutes after test compound. Mean time to anesthesia was
calculated. Examination of spontaneous motility was assessed by
administering test compound by gavage to 6 mice per dose level
(including dose levels of 1.0 and 4.0 mg/kg bw in addition to those
noted above) and recording motility every 5 minutes for 25 minutes.
Behaviour was assessed in mice by administering test compound
(including a dose level of 1.0 mg/kg bw) to 3 mice per dose to mice
which had been given glucose solution rather than food pellets the
previous night. Behavioural characteristics were assessed 30, 60
and 180 minutes after dosing. An "open field" test was conducted by
treating 10 mice with 2.5 mg amphetamine/kg bw 15 minutes after they
had received the test substance. Movement was quantitated after 30,
60 and 120 minutes. Finally, 5 mice were treated with reserpine
(5 mg/kg bw i.p.) and administered test compound 3 hours later.
Spontaneous activity and ptosis were assessed.
Triadimenol was found to potentiate hexabarbital anesthesia in
mice at all dose levels. Increased spontaneous motility was
observed with test compound alone at all dose levels except
1.9 mg/kg bw. Results were comparable between test compound and
caffeine with respect to increased motility at a given dose level.
Dose levels of 3.0 mg/kg bw was found to increase irritability and
12 mg/kg increased alertness, spontaneous activity and escape
response. The "open field-2 test found increased motor activity at
dose levels of 15 mg/kg bw and greater. The NOAEL was 3.75 mg/kg bw
for this test. Antagonism of reserpine was observed at doses of
12 mg/kg bw and greater.
Rats
As part of the study discussed above (Polacek, 1983), a "novel
box" behavioural test was conducted by dosing 10 rats with test
substance (at dose levels of 0, 3, 12 and 48 mg/kg bw) and observing
behaviour from 15 to 50 minutes. A dose of 48 mg/kg bw/day induced
CNS stimulation in the rat in the "novel box" test. The NOAEL was
12 mg/kg bw.
Special studies on metabolites
Short-term and teratology studies of the triadimenol metabolite
1,2,4-triazole are available (in addition to acute studies, see
above).
In the short-term study, 15 male and 15 female Wistar strain
rats received either 0, 100, 500 or 2500 ppm of 1,2,4-triazole in
the diet for 90 days (Bomhard et al. 1979). Lower body weights
and convulsions were observed in both sexes dosed at 2500 ppm.
Decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, MCV and MCH were observed in males
dosed at 2500 ppm at the study termination. Several high dose males
exhibited centro-lobular fat infiltration of the liver parenchyma
cells. The NOAEL was determined to be 500 ppm.
In the first teratology study, three groups of 25 Wistar rats
each received either 0, 100 or 200 mg/kg bw/day of 1,2,4-triazole by
oral gavage on days 6-15 of pregnancy (Renhof, 1988a). Body weight,
food consumption and behavioural signs were recorded for dams during
pregnancy. Fetuses were delivered on day 20 of gestation and were
examined for visceral, skeletal and external abnormalities.
The weight gain of dams dosed at 200 mg/kg bw was significantly
inhibited during and after dosing. At the 100 mg/kg bw dose level,
the incidence of fetuses with what were described as "slight bone
deviations" was increased, mean fetal weights were decreased and the
number of runts per litter was increased. An increase was found in
the number of pups with undescended testicles (11 pups from 7
litters compared to 2 pups from 2 litters in the control group). At
200 mg/kg bw, increases of resorptions and malformations were noted.
Malformations that appeared to be related to test compound included
hydronephrosis, cleft palate long bone dysplasia. Six fetuses were
noted to have undescended testicle in this group. A NOAEL was not
established in this study for embryo/ fetotoxicity. The NOAEL for
maternal toxicity was 100 mg/kg.
In a summary report for the second teratology study, it was
indicated that 25 Wistar rats per group received either 0, 10, 30 or
100 mg/kg bw/day by oral gavage on days 6 through 15 of gestation
(Renhof, 1988b). Parameters that were examined were identical to
the previous study.
Weight gain in the 100 mg/kg bw/day dams was less than other
groups. There was a decrease in fetal weight in this group and a
higher incidence of runts. There appeared to be no increase in
malformations or anomalies in any groups. The NOEL for maternal and
developmental toxicity was 30 mg/kg.
Special studies on mutagenicity
A variety of mutagenicity assays have been conducted with
triadimenol using both in vivo and in vitro systems. With the
exception of a Sister Chromatid Exchange assay which could not be
replicated, all assays were negative.
Special studies on teratology
Rat
In a summary report, no embryotoxicity or teratogenicity were
noted at dose levels of 10 or 30 mg/kg bw (A:B = 80:20, 95.2%
purity) administered by gavage to 25 strain BAY:FB 30 rats.
Maternal toxicity was reported at the highest dose level in the form
of decreased body weight gain (Renhof, 1984).
A range-finding study was conducted using Wistar/HAN rats
(Becker et al. 1986a). Five rats were dosed at either 0, 10, 50
or 150 g/kg bw/day on days 6 through 15 of gestation. Animals were
sacrificed on day 21. No maternal mortalities or signs and symptoms
of toxicity were reported. Body weight gain was clearly decreased
at the high dose level during and after treatment. Body weight gain
in other treated groups was similar to, or slightly greater than, in
control animals. A high rate of post-implantation loss (41.5%) was
observed at the high dose level. No external malformations were
observed in any group and fetal body weights were decreased only in
the high dose level compared to controls.
In the primary study, groups of Wistar/HAN rats were
administered technical triadimenol by gavage on days 6 through 15
post-coitum at dose levels of 0, 30, 60 and 120 mg/kg bw/day (Becker
et al. 1987a). Test material (purity 97.0%, A:B = 80:20) was
administered in distilled water with 0.5 cremophor EL as an
emulsifier. A total of 24, 25, 23 and 23 dams were utilized for the
0, 30, 60 and 120 mg/kg groups. Rats had been naturally mated until
a positive vaginal smear or a post-copulation plug was observed and
that day was designated as day 0 post-coitum. Body weights were
recorded daily, food consumption on days 6, 11, 16 and 21, and
clinical observations at least twice daily. All animals were
sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation on day 21 and the fetuses delivered
TABLE 2. MUTAGENICITY STUDIES ON TRIADIMENOL
CONCENTRATION
TEST SYSTEM TEST OBJECT OF TRIADIMENOL PURITY RESULTS REFERENCE
Lymphoma forward Mouse L5178Y cells 3.91-150 ug/ml 97.5% Negative Cifone, 1982
mutation assay (*)
Gene mutation (*) E. coli pol. A+, pol. A- 62.5-1000 ug/plate 97.5% Negative Herbold, 1981
Ames (*) S. typhimurium TA98, 4-2500 ug/plate 93.7% Negative Herbold, 1979b
TA100, TA1535, TA1537
Dominant lethal Mice 500 mg/kg 93.7% Negative Herbold, 1978a
Micronucleus Mice (NMRI bone marrow 2 x 350 mg/kg 93.7% Negativeq Herbold, 1978b
cells) 2 x 175 mg/kg
Micronucleus Mice (NMRI bone marrow 2 x 500 mg/kg 96.5% Negative Herbold, 1979a
cells) 2 x 350 mg/kg
Unscheduled DNA Rat hepatocytes .25-50 ug/ml 97.5% Negative Myhr, 1982
synthesis
Sister chromatid Chinese hamster ovary 38-225 ug/ml 93 Negative Putman, 1987
exchange cells
Sister chromatid Chinese hamster ovary 300 ug/ml 93 Equiv/Neg. Putman, 1982
exchange cells
Rec-assay Bacillus subtilis .05-10 mg/disk Negative Tanahashi & Miriya
NIG 45, 17 1982
(*) With and without metabolic activation.
by cesarian section. Gross pathological examination was conducted
on all dams, the uterine examined and corpora lutea and resorptions
were counted. All fetuses were weighed, sexed, and examined
grossly. One half of the fetuses were examined viscerally and the
remaining fetuses were cleared, stained and examined for skeletal
abnormalities.
No maternal deaths occurred during the course of the study.
The only clinical observation was a bloody vagina in one female of
the high dose group. No abnormal findings were noted in dams upon
necropsy. Mean body weights of treated groups were somewhat less
than the control groups at all times, including prior to dosing.
Body weights were significantly less at dose levels of 60 and
120 mg/kg than controls from day 7 (at 120 mg/kg) or day 8 (at
60 mg/kg) until day 18. Food consumption was significantly reduced
in all groups receiving test compound from day 6 to day 11. Reduced
food consumption continued to be evident in groups 3 and 4 until
study termination. Numbers of live fetuses, fetal weights, sex
ratios were similar at all dose levels. The number of embryonic
resorptions was increased at the high dose level (11.1% of total
implants compared to 5.9, 5.3 and 6.6% in the 0, 30 and 60 mg/kg
dose levels).
A variety of skeletal abnormalities were observed with an
elevated, but not dose-related, incidence in each treated group
compared to controls. A total of 5 fetuses (3.4%) from 4 litters
were affected in the control, 10 fetuses (6.6%) from 8 litters in
the low dose group, 16 fetuses (11.5%) from 12 litters in the
mid-dose group and 9 fetuses (6.7%) from 7 litters in the high dose.
Findings consisted primarily of abnormal ossification and
dumb-bell-shaped vertebrae. One case of hydrocephalus was observed
in both the control and low dose groups. One fetus evidenced
kyphosis and one multiple defects in the low dose group. No
malformations were observed in the mid or high dose groups. The
rate of skeletal malformations and/or anomalies was 0.99% in the
historical control population of 8492 (time period not specified).
The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 30 mg/kg bw based on reduced
food consumption and body weight gain at 60 and 120 mg/kg bw and
that the test compound did not reveal a teratogenic or embryotoxic
potential up to and including the highest dose tested.
In another rat teratology study, Long Evans FB 30 rats were
administered either 0, 10, 30 or 100 mg/kg bw (purity 93.7%, A:B =
60:40) by gavage on days 6 through 15 of gestation (Machemer, 1977).
Animals were naturally mated and the day that a positive vaginal
smear was found was considered to be day 0 of gestation. Twenty
animals at each dose level delivered litters for evaluation.
Animals were weighed during the treatment period and at the end of
gestation. Dams were examined at unspecified intervals. On day 20,
dams were sacrificed, the uterus examined and the fetuses and
litters were weighed. One-third of the fetuses at each dose level
were viscerally sectioned using the method of Wilson, two-thirds of
the fetuses were examined for skeletal abnormalities. All fetuses
were examined externally for malformations.
No compound-related effects on the appearance of the dams were
reported. No mortalities occurred. Weight gain was reported to be
significantly depressed during the treatment period although
individual data was not presented. A significant decrease in the
number of implantations was noted in the low dose group when
compared to controls, no effect was observed at other dose levels.
Four malformations in 3 litters were noted in the control group, 5
malformations in 2 litters in the low dose and 13 malformations in 3
litters was noted in the mid dose group. No malformations were
reported in the high dose group. Although data were not reported
for individual fetuses and neither group nor individual specific
variations were identified, the NOAEL for embryo/fetal toxicity
appeared to be 100 mg/kg bw and the NOAEL for maternal toxicity was
30 mg/kg bw based on decreased weight gain throughout gestation.
Rabbits
A range-finding study was conducted in Chinchilla hybrid
rabbits (Becker et al. 1986a). Dams were administered either 0,
50, 150 or 300 mg/kg bw of technical triadimenol (purity 97.0%, A:B
= 80:20) on days 6 through 18 post-coitum (3 per dose level for all
groups although only one rabbit at the high dose level delivered
live fetuses). One dam died at high dose level. Salivation,
dyspnea and abnormal posture were observed in dams at the high dose
level. Slight decreases in body weight gain and food consumption
were noted in the low and mid dose levels (although not
dose-related). Weight loss was noted at the high dose level. Total
post-implantation loss was noted in one of the two surviving dams at
the high dose. One malformed dead fetus was found upon external
examination of the uterine contents from a dam at the 150 mg/kg bw
dose level. Visceral and skeletal examinations were not conducted.
In the primary rabbit teratology study, groups of Chinchilla
hybrid rabbits were administered by daily gavage either 0, 8, 40 of
200 mg/kg bw triadimenol technical (97% purity, A:B = 80:20) in
water with 0.5% cremophor as an emulsifier on days 6 through 18
post-coitum (Becker et al. 1986b). Rabbits had been naturally
mated and the day mating was observed was recorded as day 0
post-coitum. A total of 16 pregnant rabbits served as the control
population and 15 rabbits in each of the remaining groups. All
animals were weighed daily, food consumption was measured on days 6,
11, 15, 19, 24 and 28. Clinical observations were recorded at least
twice daily. On day 28 of gestation, all rabbits were sacrificed
and fetuses delivered by Cesarean section. All fetuses were
examined externally, viscerally and cleared, stained and examined
for skeletal anomalies. Dams were subject to gross pathologic
examination, the uteri weighed and numbers of corpora lutea and
resorptions were recorded.
Maternal toxicity was observed at 200 mg/kg bw in the form of
CNS stimulation one-half hour to 6 hours after dosing, local areas
of hair loss, decreased food consumption and body weight gain.
There were no mortalities in any group. A marginal decrease in body
weight gain was observed at 40 mg/kg day. No other effects
attributed to test compound were noted at this dose level or at
8 mg/kg bw.
Post-implantation loss was elevated at 200 mg/kg bw with the
percentage of resorptions increasing from 3.8% per dam in the
control population to 12.8% in the 200 mg/kg bw group. Slight
reductions were observed in group mean body weight and litter mean
body weight in the high dose group. No malformations or anomalies
were observed in the control fetuses. A total of 3 fetuses from 3
litters, 2 fetuses from the same litter and 7 fetuses from 7 litters
were diagnosed with a variety of developmental abnormalities,
consisting primarily of ossification defects in the sternebrae and
vertebrae. The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 8 mg/kg bw/day
based on slightly decreased weight gain. A teratogenic potential
was not observed at dose levels as high as 200 mg/kg bw/day. The
NOAEL for fetotoxicity was 40 mg/kg bw based on increased
resorptions.
A teratology study had been previously conducted using New
Zealand rabbits (Korte & Osterburg, 1980). Groups of animals were
naturally mated and after a positive vaginal smear (considered as
gestation day 0), animals received HCG. On days 6 through 18 after
mating, 0, 10, 30 or 100 mg/kg bw (purity 97%, A:B = 80:20) was
administered by oral gavage in a water vehicle with cremophor EL as
an emulsifier. Although between 18 and 21 rabbits were inseminated
in each group, only 13, 10, 10 and 11 rabbits delivered live
offspring in the 0, 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg dose groups (2 animals in
the low dose and one each at the mid and high dose had complete
mortality of the litter). Two high dose animals died during the
course of the study with postmortem evidence of pneumonia. Body
weights were measured on days 0, 6, 18 and 28. After sacrifice,
gross autopsy was performed on each maternal animal. The number of
corpora lutea, implantations, live and dead fetuses were recorded.
All fetuses were examined for external, visceral and skeletal
abnormalities.
Body weight was slightly (but significantly) decreased in
females at the high dose level during the period of days 6-18. No
other indications of toxicity were observed in the dams. No
malformations of any type were observed in any of the fetuses. A
high incidence (ranging from 83 to 90%) of minor skeletal variations
were observed in each group. There was no apparent compound effect
on the incidence or pattern of these variations. The NOAEL for
maternal toxicity is 30 mg/kg bw in this study. The NOAEL for
fetotoxicity/ teratogenicity is 100 mg/kg bw.
Observations in humans
A statement was submitted which noted that "no adverse effects
on production workers engaged in the manufacture of the
(triadimenol) have been observed by us" (Kollert, 1981). Another
statement noted "no cases of health impairment were observed by us
with the periodically medically supervised employees (males and
females) which are involved in the formulation of BAYTAN applying
the usual safety measures" (Miksche, 1981).
COMMENTS
The two optical isomers of this chemical are both rapidly
absorbed and excreted, with slightly more of each isomer excreted in
urine by males than females. Hydroxylation of the tert-butyl
moiety and subsequent oxidation to carboxylic acid is the primary
route of metabolism. Although one of the two specific isomers is
about 10 times more acutely toxic than the other, no differences in
short-term toxicity were found in tests of the 80:20 and 60:40
mixtures of isomers in rats.
Triadimenol has a low acute toxicity in the species examined.
Several short-term studies have been conducted in rats. At
higher doses increased liver weights and liver hypertrophy were
observed. The NOAEL was 120 ppm, equal to 8 mg/kg bw/day.
Three short-term dog studies have been conducted. The NOAEL
was 100 ppm in the diet (equal to 7.5 mg/kg bw/day) based on
hepatotoxicity at the higher dose levels.
A long-term toxicity study was conducted in mice. An increased
incidence of hyperplastic nodules in the liver was observed in
females at 2000 ppm (equivalent to 300 mg/kg bw/day). There was an
increased incidence of liver tumours in females at the 500 and
2000 ppm levels (equivalent to 75 and 300 mg/kg bw/day). A NOAEL
could not be established for this study since aspartate
amino-transferase was elevated in all treated groups in a
dose-dependent manner.
No increases in any tumour type were observed in a long-term
feeding study in rats. Hepatotoxicity was observed at 500 ppm and
above. The NOAEL was 125 ppm (equal to 7 mg/kg bw/day).
In a 2-generation, 2 litters per generation reproduction study
in rats, the NOAEL was 125 ppm in the diet, equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day.
Decreased parental pup body weights were observed at a dose level of
500 ppm. Teratology studies were conducted in rats and rabbits. An
increased rate of resorption was found at the high dose in the rat
study (120 mg/kg bw/day) and rabbit study (200 mg/kg bw/day). The
NOAELs for embry-fetotoxicity were 60 mg/kg bw/day in the rat and
40 mg/kg bw/day in the rabbit.
After reviewing all available in vitro and in vivo
short-term tests, the meeting concluded that there was no evidence
of genotoxicity.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat: 125 ppm in the diet, equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day (based
on reproductive effects)
Dog: 100 ppm in the diet, equal to 7.5 mg/kg bw/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for humans
0-0.05 mg/kg bw.
Studies which will provide information in the continued evaluation
of the compound
Observations in humans.
REFERENCES
Becker, H., Frei, D. & Sachsse, K. (1986a) Dose-finding
embryotoxicity including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rabbit. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R 3692.
Becker, H., Frei, D. & Sachsse, K. (1986b) Dose-finding
embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rabbit. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Unpublished Report No. R 3826
submitted to WHO by Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Becker, H., Frei, D., Vogel, W. & Terrier, C. (1987a)
Embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rat. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R3988.
Becker, H., Mueller, E., Vogel, W. & Terrier, C. (1987b)
Embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rat. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R4145.
Bomhard, E. & Löser, E. (1982) KWG 0519 - Chronic toxicological
study on mice (feeding experiment over two years). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 10855.
Bomhard, E., Löser, E. & Schilde, B. (1979) 1,2,4-triazole.
Subchronic toxicological study with rats (feeding study over three
months). Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 8667.
Cifone, M.A. (1982) Mutagenicity evaluation of KWG 0519 in the
mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay. Litton Bionetics, Rockville,
Maryland. Report No. R 2204.
Flucke, W. (1981) KWG 0519 - Study of sensitization effect on
guinea pigs. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 9894.
Flucke, W. (1979a) KWG 0519 - Form A - Determination of acute
toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG.
Flucke, W. (1979b) KWG 0519 - Form B - Determination of acute
toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG.
Flucke, W. (1979c) KWG 0519 (Mixture of isomers) - Determination of
acute toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Heimann, K.G. (1985a) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13616.
Heimann, K.G. (1985b) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13617.
Heimann, K.G. (1985c) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13618.
Heimann, K.G. & Schilde, B. (1984) KWG 0519 - Subacute dermal
toxicity study on rabbits. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12496.
Herbold, B. (1981) KWG 0519 Triadimenol - The active ingredient of
Baytan. Study of DNA damage using the E. coli Pol-A1 test.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 102265.
Herbold, B. (1979a) KWG 0519 - Micronucleus test on mouse to
evaluate KWG 0519 for potential mutagenic effects. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 8584.
Herbold, B. (1979b) KWG 0519 - Salmonella/microsome test for
detection point -mutagenic effects. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer
AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 8189.
Herbold, B. (1978a) KWG 0519 - Dominant lethal study on male mouse
to test for mutagenic effects. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7900.
Herbold, B. (1978b) KWG 0519 - Micronucleus test on mouse to
evaluate KWG 0519 for potential mutagenic effects. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7588.
Hoffmann, K. & Vogel, O. (1984) KWG 0519 - First chronic study of
toxicity to dogs on oral administration (two-year feeding study).
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 12970.
Hoffmann, K. (1984) KWG 0519 - Second chronic study of toxicity to
dogs on oral administration (six-month feeding study). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12971.
Hoffmann, K. & Kaliner, G. (1977) KWG 0519 - Subchronic toxicity
study on dogs (thirteen-week feeding experiment). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6633.
Kimmerle, G. (1976) KWG 0519 - Subacute inhalation toxicity study
on rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 6321.
Kollert, W. (1981) BBA-requirement/effect on humans. Medical
Department EL, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Korte, R. & Osterburg, I. (1980) Embryotoxicity of KWG 0519 in
rabbits. Reprotox GmbH, Munster, FRG. Report No. R 1901.
Krötlinger, F., Löser, E. & Schilde, B. (1982) KWG 0519 - Chronic
toxicity study on rats (2-year feeding experiment). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 11009.
Leeling, J.L., Helms, R.J., Polomcak, S.C. & Craigo, L.A. (1988)
Dermal absorption of triadimenol-14C in rats. Miles, Inc.,
Elkhart, Indiana. Report No. Mobay 1055.
Löser, E. & Kaliner, G. (1977) KWG 0519 - Subchronic toxicity study
on rats (three-month feeding experiment). Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6811.
Löser , E. & Eibenm R. (1984) KWG 0519 - Two-generation study on
rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Report No. 12390.
Machemer, L. (1977) KWG 0519 - Evaluation for embryotoxic and
teratogenic effects on orally dosed rats. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7038.
Mihail, F. & Vogel, O. (1981) Study of comparative toxicity to rats
after 4-week administration using two test compound samples.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 9949.
Mihail, F. & Thyssen, J. (1980) KWG 0519 - Acute toxicity studies.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 9451.
Polacek, I. (1983) Central nervous effects of KWG 0519 (Pilot
study). Toxicological Institute, Bayer AG, Regenburg, FRG. Report
No. 2695.
Puhl, R.J. & Hurley, J.B. (1978) The metabolism and excretion of
Baytan by rats. Mobay Chemical Company, Stilwell, Kansas. Report
No. 66489 (FM 209).
Putman, D.L. (1987) Sister chromatid exchange assay in Chinese
hamster ovary (CHO) cells. Microbiological Associates, Rockville,
Maryland. Report No. 1022.
Renhof, M. (1984) KWG 0519 - Study for embryotoxic effects on rats
after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12687.
Renhof, M. (1988a) 1,2,4-triazole - Investigations into embryotoxic
effects on rats after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 17402.
Renhof, M. (1988b) 1,2,4-triazole - Investigations into embryotoxic
effects on rats after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 17401.
Tanahashi, N. & Moriya, M. (1982) Triadimenol - Microbial
mutagenicity study. Department of Toxicology, Institute of
Environmental Toxicology, Tokyo, Japan.
Thyssen, J. & Kaliner, G. (1976) KWG 0519 - Subacute oral
cumulative toxicity study on rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer
AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6481.
Thyssen, J. & Kimmerle, G. (1976a) KWG 0519 - Acute toxicity
studies. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer, AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 6090.
Thyssen, J. & Kimmerle, G. (1976b) 1,2,4-triazole. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer, AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 5926.
A dermal absorption study was conducted in Charles River Crl:CD
rats using 14C ring-labelled triadimenol (15.78 mCi/mM) (Leeling
et al. 1988). Twenty-four animals per dose level were dosed with
either .01, .1, 1 or 10 mg of test material on a 15 cm2 area of
shaved skin (equivalent to .04 to 40 mg/kg bw). Test material was
covered by a gauze patch after application. Four animals per dose
level were bled and then sacrificed at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8 and 24 hours
after dosing. Urine and feces were collected from each animal.
Radioactivity was also determined in whole carcass, skin wash and
excised skin. Dermal absorption was rapid. It was estimated that
50% of test material was likely to be absorbed and that absorption
was somewhat slower at higher concentrations (with half-lives for
elimination ranging from 27 hours at the low dose to 86 hours at the
high dose), suggesting a saturation of transport.
Toxicological studies
Acute toxicity
See Table 1.
In addition to the acute studies shown in the table above, skin
and eye irritation studies (Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b) and skin
sensitization studies (Flucke, 1981) were submitted for triadimenol.
All were considered to be "negative". Although no skin irritation
was observed in either man or the rabbit with 1, 2, 4-triazole, it
was found to be "strongly irritating" to the eye of the rabbit
(Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b).
Short-term studies
Rats
Groups of 10 albino Wistar II strain rats were exposed by
inhalation to triadimenol at concentrations averaging 0, 30.39
(26.8-31.8), 68.03 (61.2-73.0) and 229.71 (201-255) mg/m3 for 6
hours per day for 3 weeks (Kimmerle, 1976). Measurements were
gravimetric and concentrations reported are actual rather than
nominal. Control animals were exposed to only the
ethanol/polyethylene glycol solvent. No compound-related effect was
observed on any parameter examined. The NOAEL was 229.71 mg/m3.
TABLE 1. RESULTS OF ACUTE TOXICITY TESTING OF TRIADIMENOL AND METABOLITES
COMPOUND LD50
ADMINISTERED SEX SPECIES ROUTE (mg/kg bw) REFERENCE
Form A M Rat oral 579 Flucke, 1979a
Form B M Rat oral 5000 Flucke, 1979b
Forms A/B 60:40 M Rat oral 819 Flucke, 1979c
M Rat oral 897 Flucke, 1979c
Forms A/B 60:40 M Rat oral 1161 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
F Rat oral 1105 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M Rat i.p. 367 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
F Rat i.p. 352 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M&F dermal >5000 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
M&F Rat inhalation >305 mg/m3 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976a
(4 hrs)
Forms A/B 80:20 M Rat oral 689 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat oral 752 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat oral 1098 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
F Rat oral 1037 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M Rat i.p. 371 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
F Rat i.p. 286 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M&F Rat dermal >5000 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
M&F Rat inhalation >1557 mg/m3 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
(1 hour)
TABLE 1 (contd.)
COMPOUND LD50
ADMINISTERED SEX SPECIES ROUTE (mg/kg bw) REFERENCE
Rat, inhalation M&F Rat inhalation >954 mg/m3 Mihail & Thyssen, 1980
Metabolite M Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985a
KWG 1640 N F Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985a
Metabolite M Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985b
KWG 1342 N F Rat oral >1000 Heimann, 1985b
Metabolite M Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985c
KWG 1323 N F Rat oral >5000 Heimann, 1985c
1,2,4-triazole M Rat oral 1650 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
F Rat oral 1648 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
M Rat dermal 4200 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
F Rat dermal 3129 Thyssen & Kimmerle, 1976b
Two subchronic rat studies of 90 days duration have been
conducted. In the first, fifteen SPF Wistar rats per sex/dose were
fed diets containing either 150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol
technical (98% purity, A:B = 60:40) for 90 days (Löser & Kaliner,
1977). Thirty male and 30 female animals were fed control diet.
The rats were 28 to 32 days old at the start of the study.
One female rat in the mid-dose group died during the course of
the study. There was no compound-related effect on physical
appearance or behaviour or food consumption. Body weights of high
dose males and females were slightly but significantly depressed
during the course of the study. Several changes in hematology
parameters were significantly different at 2400 ppm: lower
hematocrit percent volume in females at one month, lower MCH and MCV
in males at 3 months, lower HCT in females at 3 months and a lower
hematrocrit percent volume in females at 3 months. Other hematology
and clinical chemistry and urinalysis findings were considered by
the authors to not be related to treatments. Absolute liver weights
of high dose males and females were elevated as were kidney and
ovary weights in high dose females. No histopathological changes
were considered to be related to test compound administration. The
NOAEL in this study was 600 ppm.
In the second 90 day rat study, Crj:CD rats obtained from
Charles River, Japan, were fed diets containing either 0, 120, 600
or 3000 ppm triadimenol technical (94% purity, A:B = 80:20) for 90
days (Nishimura & Nobuo, 1983). Twenty males and 20 females were
used at each dose level. Dose levels corresponded to 89.0, 39.6 and
208.5 mg/kg bw/day for males and 9.4, 46.4 and 221.1 mg/kg bw/day
based on food consumption measurements.
Piloerection and depilitation were observed at the high dose
level early in the study, no compound-related clinical observations
were noted in other groups or after the first month in the high dose
group. Body weight and food consumption were decreased only at the
high dose level. Urinalysis findings were unremarkable.
Significant decreases in hematocrit, hemoglobin and platelet counts
were noted in high dose males and females. Significantly lower
reticulocyte counts were noted in the mid and high dose groups of
both sexes. Because there were not corresponding histological
changes in the spleen and bone marrow, these findings were judged
not to be compound-related. Several parameters suggestive of
hepatotoxicity were affected at the highest dose level in this study
- eosinophilic degeneration of hepatocytes, fatty changes and
changes in triglycerides, free fatty acids, total cholesterol,
phospholipid, total protein, A/G ratio and albumin. The fatty
changes were observed primarily in the central to midzonal region in
male animals and in the peripheral region in female animals.
Increased absolute and relative liver weights were observed at both
the mid and high dose levels in both sexes. Several rats at both
dose levels had livers diagnosed as hypertrophic or as having a
"pronounced lobular pattern". Other changes in histology and in
other parameters were not considered to be compound-related. The
NOAEL was 120 ppm, equal to 8.0 for males and 9.4 for females for
this study.
In a comparison of the short-term toxicity of two ratios of
isomers, 20 SPF Wistar albino rats/sex/dose were given by oral
intubation either 0, 15, 45 or 100 mg/kg bw/day of 80:20 (A:B) or 45
or 100 mg/kg bw/day of 60:40 (A:B) for 4 weeks (Mihail & Vogel,
1981). One half of each group was sacrificed at the end of 4 weeks
and one half was observed for an additional 4-week recovery phase.
Liver enzymes (N- and O- demethylases and cytochrome P-450) were
determined at sacrifice.
All treated groups except those receiving 15 mg/kg bw/day
exhibited slightly increased CNS activity after administration of
test compound which lasted for approximately 2 hours after dosing.
The only other compound-related effects were on cytochrome P-450 and
N- and O-demethylase. Each of the induced enzymes returned to
control levels by the end of the recovery period. N-demethylase was
induced to a slightly greater extent by the 80:20 mixture,
cytochrome P-450 was slightly more induced by the 60:40 mixture.
There were no important toxicological differences between the
mixtures.
In a 4 week rat study, 20 male and 20 female Wistar II strain
albino rats were dosed by gavage with either 0, 1.5, 5, 15 or
45 mg/kg bw/day of technical material (98.5%) (Thyssen & Kaliner,
1976). One half of the animals in each group was kept under
observation for an additional 28 days before sacrifice.
No mortalities occurred and no compound-related behavioural
effects were noted. Body weights were similar in all groups. No
compound-related effects on clinical chemistry, hematology,
urinalysis, organ weight, gross or histopathology were observed.
Absolute and relative thyroid weights (male and female combined)
were significantly increased at 28 days but returned to normal at 56
days. The NOAEL was found to be 45 mg/kg bw/day (the highest dose
tested) in this study.
Rabbits
Groups of 6 New Zealand rabbits were exposed dermally for 6
hours to either 0, 50 or 250 mg/kg bw/day of test material (98%
purity) (Heimann & Schilde, 1984). Skin was clipped for all animals
and abraded for 3 animals per sex/dose prior to treatment. Material
was applied dissolved in distilled water with cremophor as an
emulsifier for 15 consecutive days. There were no indications of
topical or systemic effects which appeared to be compound-related.
The NOAEL was therefore 250 mg/kg bw/day.
Dogs
The first of three short-term toxicity studies in the dog was
conducted utilizing 4 male and 4 female beagle dogs per dose level
(Hoffmann & Kaliner, 1977). Dogs were fed diet containing either 0,
150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol technical (98.5% purity, A:B =
60:40) for 13 weeks. At the start of the study, the animals weighed
between 6.9 and 9.5 kg and were between 24 and 30 weeks old.
No mortalities were observed during the course of the study.
Occasional vomiting was observed after administration of the test
compound, no other clinical observations appeared to be
compound-related. There were no effects on reflexes, body
temperature, pulse or ophthalmology. There were no marked
differences between control animals and treated regarding water or
food intake. There was a slight depression of body weight gain in
both male and female groups at the high dose level compared to
control groups. Differences in hematological parameters between
groups did not appear to be compound-related. Several enzymatic
effects were as a consequence of test compound administration. GPT
levels were increased in a number of dogs in the mid and high dose
groups at the 6 and 13 week measurements. AP levels were generally
higher than controls in all treated groups both at the intermediate
and final measurements. Plasma cholesterol levels were also higher
in the mid and high dose groups both at the intermediate and final
measurements. Cytochrome P-450 and N-demethylase were elevated only
in the high dose group. Relative liver weights were increased in
both males and females at the high dose level. Absolute kidney
weights were also elevated in males at the high dose. No
histological changes were observed that were attributable to
treatment. The NOAEL was 600 ppm (equivalent to 45 mg/kg bw/day).
Purebred beagle dogs 32 to 36 weeks old and 7.5 to 12.5 kg in
weight, were randomized and divided in groups of 4 dogs/sex/dose
level and administered either 0, 150, 600 or 2400 ppm of triadimenol
technical (95% purity, A:B = 60:40) via the diet for 104 weeks
(Hoffmann & Vogel, 1984).
One female was sacrificed in moribund condition (in the high
dose group) during the course of the study but this was not
attributed to treatment. Clinical observations, tests of reflexes,
ophthalmoscopic observations, body weights and food intake were not
affected by treatment. However, body weights of all treated groups
were consistently lower than the control groups. This was
attributed to the unusually great body weight gain in both male and
female control groups. Hematological parameters that were examined
differed randomly and no effect of test compound was evident.
Elevated AP activity was noted in 4 high dose animals over the
course of the study. Slightly increased N-demethylase and
cytochrome P-450 were noted in the high dose group. Urinalysis
findings were similar in all groups. Organ weights were not affected
by treatment. No gross or histological findings were attributed to
treatment. A NOAEL cannot be established in this study due to an
apparent decrease in body weight gain in all treated groups.
A third feeding study in the dog was conducted using 6
animals/sex/dose (Hoffmann, 1984). The study was of 6 months'
duration and used dose levels of 90, 10, 30 and 100 ppm (purity
98.0%, A:B = 80:20). Parameters examined were identical to those in
the study discussed above with the exception of histology, for which
no examination took place. No effects were attributed to test
compound at the highest dose tested (equivalent to 7.5 mg/kg bw).
Long-term/carcinogenicity studies
Mice
Strain CF1/W 74 mice were administered triadimenol (A:B = 80%
premix) for 24 months in a combined oncogenicity/long-term toxicity
study (Bomhard & Löser, 1982). A total of 50 mice/sex/dose level
were fed diet containing either 0, 125, 500 or 2000 ppm of technical
triadimenol (95% purity) starting at 5 to 6 weeks of age. Animals
were examined daily, and were weighed weekly for the first 15 weeks
and every 3 weeks thereafter. Food consumption and concentration of
test compound was measured regularly. Clinical chemistry
measurements and hematological measurements were conducted at 0, 12
and 24 months. Gross pathological examination was conducted on all
animals dying or sacrificed. Heart, lungs, liver, spleen, kidney
and testicles were weighed. In addition to the weighed organs,
brain, pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, stomach, pancreas, urinary
bladder, ovaries and uterus, femur with skeletal muscle and nerve
were fixed, stained and examined histopathologically for all
animals.
Actual doses, based on food consumption measurements, were 30,
140 and 620 mg/kg bw/day for male mice and 50, 200 and 810 mg/kg
bw/day for female mice. Transient depressions of body weight gain
were observed in the low dose group. Consistent depression of body
weight gain was observed in males and females of both the mid and
high dose groups with the extent of depression somewhat greater in
male than in female mice. No group showed any apparent signs of
toxicity. Mortality was similar in all groups and ranged from 20 to
32% at 18 months and 62 to 78% at 24 months. Hematological
parameters did not appear to be affected by treatment.
Significantly elevated GOT was observed in male mice at the high
dose level and in female groups receiving test compound at 12
months. GPT was elevated and cholesterol depressed for the high
dose levels of both sexes at 12 months. SAP was elevated for mid-
and high dose male animals and total protein was depressed at the
interim measurement. At 24 months, GPT was slightly elevated in the
low dose and significantly elevated in the mid- and high dose levels
of both sexes. GOT was elevated in all treated groups, significantly
in low and high dose males and in mid- and high dose females. Other
clinical chemistry changes were not considered to be toxicologically
significant.
Organ weights were similar between groups with the exception of
liver weights, which were elevated in both sexes at the high dose
level. Females at the high dose level had a slightly increased
incidence of hyperplastic nodules (7 compared to 2 in the control
group) and there were more hyperplasias of the liver in high dose
males (5) than in the control group (2). No increase was observed
in total tumour incidence or the number of tumour-bearing animals.
A significantly higher incidence of liver adenomas was observed in
high dose females (6 adenomas compared to 0 adenomas and 1
adenocarcinoma in the control group). No liver tumours were noted
in the low dose and 4 adenomas and 1 adenocarcinoma were observed in
the mid dose group. This corresponds to an incidence of 2.3, 0,
10.4 and 12.3% for the 0, 125, 500 and 2000 ppm groups,
respectively. A higher incidence of thyroid cysts was noted in the
high dose males dying during the course of the study (5) than in
controls or in any other treated group (2 per group). Two
nonepithelial carcinosarcomas (a relatively rare tumour) were
observed in high dose males. The incidence of other neoplastic and
non-neoplastic findings were similar in all groups. Aspartate
aminotransferase (GOT) was elevated in all treated groups and the
increased incidence of liver tumours in mid and high dose females,
both of which appear to be compound-related. A NOAEL could not be
established for this study.
Rats
SPF rats of the strain BOR:WISW were administered test compound
(94.9% purity, A:B = 60:40) in the diet for 24 months at dose levels
of either 0, 125, 500 or 2000 ppm (Krötlinger et al. 1982). Each
dose level consisted of 60 males and 60 females. All animals were
observed daily. Body weights were recorded weekly until week 26;
afterwards, they were recorded every two weeks. Food consumption
was measured weekly. Urinalysis, hematology and clinical chemistry
measurements were conducted on 10 males and 10 females per dose
level at 3, 6, 12 and 24 months. All animals were examined grossly.
Thyroid, heart, lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys, adrenals, testes and
ovaries were weighed. In addition to the above tissues, the
following were examined microscopically for all animals: aorta,
eyes, intestine, femur, muscle, nerve, brain, urinary bladder,
pituitary, lymph nodes, stomach, spleen, epididymides, adrenals,
seminal vesicles, sternum, trachea and uterus. All grossly
remarkable tissues were examined histologically.
Survival during the course of the study was good with only 13%
to 30% mortality by the end of 24 months. Body weights of both
males and females at the high dose level were depressed during most
of the study compared to the respective control groups. Test
compound intake, taking into account food consumption, averaged 7,
25 and 105 mg/kg bw/day for males and 9, 35 and 144 mg/kg bw/day for
females. Although RBC counts were low for the high dose females and
males compared to the controls, the study authors noted that these
were within the physiologically normal range. Other hematological
parameters were similar in treated and control animals. GOT and GPT
were generally elevated in both males and females in the mid and
high dose levels during the course of the study. A slight elevation
in these parameters was observed in the low dose level animals
throughout the study which did not achieve statistical significance.
SAP was elevated only at the 12 month measurement in high dose
females. Other clinical chemistry parameters were not considered to
be affected by treatment. Both absolute and relative liver weights
were elevated in high dose females. Although both relative and
absolute ovarian weight was decreased in high dose females, these
and other organ weight changes (except for liver) were considered
random or the consequence of lower body weights in the high dose
group.
No gross pathological observations were noted that appeared to
be attributable to test compound. The most common tumour types were
pituitary and thyroid adenomas, adrenal pheochromocytomas, Leydig
cell tumours and uterine adenocarcinomas. No tumour type appeared
to be compound-related. The total number of tumours and the total
number of malignant tumours was similar in each group. No
non-neoplastic histopathological findings could be attributed to
treatment. The NOAEL was 125 ppm, equal to 7 mg/kg bw in males and
9 mg/kg bw in females.
Reproduction studies
Rats
A two-generation reproduction study was conducted in strain
BOR: WISW SPF rats (Löser & Eiben, 1984). Ten males and 20 females
were fed test compound (97.5% purity, A:B = 80:20) for 100 days
prior to the first mating at dose levels of 0, 20, 100 and 500 ppm.
Animals were weighed at weekly intervals before and after mating.
F0 animals were weighed at 3-day intervals during mating. F1b
females were weighed 1, 6, 15 and 20 days after insemination.
Animals were caged together for 5 days during mating and vaginal
smears were taken daily. The F1b litter was used to produce the
second generation. The F1a, F2a and F2b pups were lactated for 4
weeks after birth and sacrificed. Fertility, gestation, viability,
lactation and insemination indexes were calculated. Animals dying
during the course of the study and F2b pups and F1b parents were
grossly examined after sacrifice. The F1b parents had the
following organs weighed: liver, kidney, testicle and ovary.
Histopathological examination was conducted on tissues from the high
dose and control groups of F1b parents and 10 F2b male and 10 F2b
females.
Behaviour and mortality were not affected by treatment. Mean
group body weights were similar at all dose levels in the F0
generation but were depressed in the high dose level parental
animals of the F1b group and in F2a pups. Food consumption was also
slightly less for this group. There were no significant differences
between groups with regard to food intake. The fertility index,
mean litter size, lactation index, viability and insemination
indexes were not affected by treatment. The mean birth weight was
significantly decreased in the high dose pups F1b generation but no
effect on birth weight was observed in the first litter or in either
litter of the second generation. No apparent compound-related
toxicity was observed in any autopsied animals. There were no
histopathological changes which appeared to be related to treatment.
No toxicologically significant organ weight changes were found. The
No Observed Effect Level was 125 ppm (equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day).
Special studies on central nervous system effects
Mice
A study to investigate the central nervous system effects of
triadimenol was undertaken (Polacek, 1983). Test compound (98%
purity) was administered by a single gavage dose at levels of 0, 3
or 3.75, 15.0 and 60.0 mg/kg bw (except as noted below).
Hexobarbital sodium was administered to 10 mice per dose level 60
minutes after test compound. Mean time to anesthesia was
calculated. Examination of spontaneous motility was assessed by
administering test compound by gavage to 6 mice per dose level
(including dose levels of 1.0 and 4.0 mg/kg bw in addition to those
noted above) and recording motility every 5 minutes for 25 minutes.
Behaviour was assessed in mice by administering test compound
(including a dose level of 1.0 mg/kg bw) to 3 mice per dose to mice
which had been given glucose solution rather than food pellets the
previous night. Behavioural characteristics were assessed 30, 60
and 180 minutes after dosing. An "open field" test was conducted by
treating 10 mice with 2.5 mg amphetamine/kg bw 15 minutes after they
had received the test substance. Movement was quantitated after 30,
60 and 120 minutes. Finally, 5 mice were treated with reserpine
(5 mg/kg bw i.p.) and administered test compound 3 hours later.
Spontaneous activity and ptosis were assessed.
Triadimenol was found to potentiate hexabarbital anesthesia in
mice at all dose levels. Increased spontaneous motility was
observed with test compound alone at all dose levels except
1.9 mg/kg bw. Results were comparable between test compound and
caffeine with respect to increased motility at a given dose level.
Dose levels of 3.0 mg/kg bw was found to increase irritability and
12 mg/kg increased alertness, spontaneous activity and escape
response. The "open field-2 test found increased motor activity at
dose levels of 15 mg/kg bw and greater. The NOAEL was 3.75 mg/kg bw
for this test. Antagonism of reserpine was observed at doses of
12 mg/kg bw and greater.
Rats
As part of the study discussed above (Polacek, 1983), a "novel
box" behavioural test was conducted by dosing 10 rats with test
substance (at dose levels of 0, 3, 12 and 48 mg/kg bw) and observing
behaviour from 15 to 50 minutes. A dose of 48 mg/kg bw/day induced
CNS stimulation in the rat in the "novel box" test. The NOAEL was
12 mg/kg bw.
Special studies on metabolites
Short-term and teratology studies of the triadimenol metabolite
1,2,4-triazole are available (in addition to acute studies, see
above).
In the short-term study, 15 male and 15 female Wistar strain
rats received either 0, 100, 500 or 2500 ppm of 1,2,4-triazole in
the diet for 90 days (Bomhard et al. 1979). Lower body weights
and convulsions were observed in both sexes dosed at 2500 ppm.
Decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, MCV and MCH were observed in males
dosed at 2500 ppm at the study termination. Several high dose males
exhibited centro-lobular fat infiltration of the liver parenchyma
cells. The NOAEL was determined to be 500 ppm.
In the first teratology study, three groups of 25 Wistar rats
each received either 0, 100 or 200 mg/kg bw/day of 1,2,4-triazole by
oral gavage on days 6-15 of pregnancy (Renhof, 1988a). Body weight,
food consumption and behavioural signs were recorded for dams during
pregnancy. Fetuses were delivered on day 20 of gestation and were
examined for visceral, skeletal and external abnormalities.
The weight gain of dams dosed at 200 mg/kg bw was significantly
inhibited during and after dosing. At the 100 mg/kg bw dose level,
the incidence of fetuses with what were described as "slight bone
deviations" was increased, mean fetal weights were decreased and the
number of runts per litter was increased. An increase was found in
the number of pups with undescended testicles (11 pups from 7
litters compared to 2 pups from 2 litters in the control group). At
200 mg/kg bw, increases of resorptions and malformations were noted.
Malformations that appeared to be related to test compound included
hydronephrosis, cleft palate long bone dysplasia. Six fetuses were
noted to have undescended testicle in this group. A NOAEL was not
established in this study for embryo/ fetotoxicity. The NOAEL for
maternal toxicity was 100 mg/kg.
In a summary report for the second teratology study, it was
indicated that 25 Wistar rats per group received either 0, 10, 30 or
100 mg/kg bw/day by oral gavage on days 6 through 15 of gestation
(Renhof, 1988b). Parameters that were examined were identical to
the previous study.
Weight gain in the 100 mg/kg bw/day dams was less than other
groups. There was a decrease in fetal weight in this group and a
higher incidence of runts. There appeared to be no increase in
malformations or anomalies in any groups. The NOEL for maternal and
developmental toxicity was 30 mg/kg.
Special studies on mutagenicity
A variety of mutagenicity assays have been conducted with
triadimenol using both in vivo and in vitro systems. With the
exception of a Sister Chromatid Exchange assay which could not be
replicated, all assays were negative.
Special studies on teratology
Rat
In a summary report, no embryotoxicity or teratogenicity were
noted at dose levels of 10 or 30 mg/kg bw (A:B = 80:20, 95.2%
purity) administered by gavage to 25 strain BAY:FB 30 rats.
Maternal toxicity was reported at the highest dose level in the form
of decreased body weight gain (Renhof, 1984).
A range-finding study was conducted using Wistar/HAN rats
(Becker et al. 1986a). Five rats were dosed at either 0, 10, 50
or 150 g/kg bw/day on days 6 through 15 of gestation. Animals were
sacrificed on day 21. No maternal mortalities or signs and symptoms
of toxicity were reported. Body weight gain was clearly decreased
at the high dose level during and after treatment. Body weight gain
in other treated groups was similar to, or slightly greater than, in
control animals. A high rate of post-implantation loss (41.5%) was
observed at the high dose level. No external malformations were
observed in any group and fetal body weights were decreased only in
the high dose level compared to controls.
In the primary study, groups of Wistar/HAN rats were
administered technical triadimenol by gavage on days 6 through 15
post-coitum at dose levels of 0, 30, 60 and 120 mg/kg bw/day (Becker
et al. 1987a). Test material (purity 97.0%, A:B = 80:20) was
administered in distilled water with 0.5 cremophor EL as an
emulsifier. A total of 24, 25, 23 and 23 dams were utilized for the
0, 30, 60 and 120 mg/kg groups. Rats had been naturally mated until
a positive vaginal smear or a post-copulation plug was observed and
that day was designated as day 0 post-coitum. Body weights were
recorded daily, food consumption on days 6, 11, 16 and 21, and
clinical observations at least twice daily. All animals were
sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation on day 21 and the fetuses delivered
TABLE 2. MUTAGENICITY STUDIES ON TRIADIMENOL
CONCENTRATION
TEST SYSTEM TEST OBJECT OF TRIADIMENOL PURITY RESULTS REFERENCE
Lymphoma forward Mouse L5178Y cells 3.91-150 ug/ml 97.5% Negative Cifone, 1982
mutation assay (*)
Gene mutation (*) E. coli pol. A+, pol. A- 62.5-1000 ug/plate 97.5% Negative Herbold, 1981
Ames (*) S. typhimurium TA98, 4-2500 ug/plate 93.7% Negative Herbold, 1979b
TA100, TA1535, TA1537
Dominant lethal Mice 500 mg/kg 93.7% Negative Herbold, 1978a
Micronucleus Mice (NMRI bone marrow 2 x 350 mg/kg 93.7% Negativeq Herbold, 1978b
cells) 2 x 175 mg/kg
Micronucleus Mice (NMRI bone marrow 2 x 500 mg/kg 96.5% Negative Herbold, 1979a
cells) 2 x 350 mg/kg
Unscheduled DNA Rat hepatocytes .25-50 ug/ml 97.5% Negative Myhr, 1982
synthesis
Sister chromatid Chinese hamster ovary 38-225 ug/ml 93 Negative Putman, 1987
exchange cells
Sister chromatid Chinese hamster ovary 300 ug/ml 93 Equiv/Neg. Putman, 1982
exchange cells
Rec-assay Bacillus subtilis .05-10 mg/disk Negative Tanahashi & Miriya
NIG 45, 17 1982
(*) With and without metabolic activation.
by cesarian section. Gross pathological examination was conducted
on all dams, the uterine examined and corpora lutea and resorptions
were counted. All fetuses were weighed, sexed, and examined
grossly. One half of the fetuses were examined viscerally and the
remaining fetuses were cleared, stained and examined for skeletal
abnormalities.
No maternal deaths occurred during the course of the study.
The only clinical observation was a bloody vagina in one female of
the high dose group. No abnormal findings were noted in dams upon
necropsy. Mean body weights of treated groups were somewhat less
than the control groups at all times, including prior to dosing.
Body weights were significantly less at dose levels of 60 and
120 mg/kg than controls from day 7 (at 120 mg/kg) or day 8 (at
60 mg/kg) until day 18. Food consumption was significantly reduced
in all groups receiving test compound from day 6 to day 11. Reduced
food consumption continued to be evident in groups 3 and 4 until
study termination. Numbers of live fetuses, fetal weights, sex
ratios were similar at all dose levels. The number of embryonic
resorptions was increased at the high dose level (11.1% of total
implants compared to 5.9, 5.3 and 6.6% in the 0, 30 and 60 mg/kg
dose levels).
A variety of skeletal abnormalities were observed with an
elevated, but not dose-related, incidence in each treated group
compared to controls. A total of 5 fetuses (3.4%) from 4 litters
were affected in the control, 10 fetuses (6.6%) from 8 litters in
the low dose group, 16 fetuses (11.5%) from 12 litters in the
mid-dose group and 9 fetuses (6.7%) from 7 litters in the high dose.
Findings consisted primarily of abnormal ossification and
dumb-bell-shaped vertebrae. One case of hydrocephalus was observed
in both the control and low dose groups. One fetus evidenced
kyphosis and one multiple defects in the low dose group. No
malformations were observed in the mid or high dose groups. The
rate of skeletal malformations and/or anomalies was 0.99% in the
historical control population of 8492 (time period not specified).
The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 30 mg/kg bw based on reduced
food consumption and body weight gain at 60 and 120 mg/kg bw and
that the test compound did not reveal a teratogenic or embryotoxic
potential up to and including the highest dose tested.
In another rat teratology study, Long Evans FB 30 rats were
administered either 0, 10, 30 or 100 mg/kg bw (purity 93.7%, A:B =
60:40) by gavage on days 6 through 15 of gestation (Machemer, 1977).
Animals were naturally mated and the day that a positive vaginal
smear was found was considered to be day 0 of gestation. Twenty
animals at each dose level delivered litters for evaluation.
Animals were weighed during the treatment period and at the end of
gestation. Dams were examined at unspecified intervals. On day 20,
dams were sacrificed, the uterus examined and the fetuses and
litters were weighed. One-third of the fetuses at each dose level
were viscerally sectioned using the method of Wilson, two-thirds of
the fetuses were examined for skeletal abnormalities. All fetuses
were examined externally for malformations.
No compound-related effects on the appearance of the dams were
reported. No mortalities occurred. Weight gain was reported to be
significantly depressed during the treatment period although
individual data was not presented. A significant decrease in the
number of implantations was noted in the low dose group when
compared to controls, no effect was observed at other dose levels.
Four malformations in 3 litters were noted in the control group, 5
malformations in 2 litters in the low dose and 13 malformations in 3
litters was noted in the mid dose group. No malformations were
reported in the high dose group. Although data were not reported
for individual fetuses and neither group nor individual specific
variations were identified, the NOAEL for embryo/fetal toxicity
appeared to be 100 mg/kg bw and the NOAEL for maternal toxicity was
30 mg/kg bw based on decreased weight gain throughout gestation.
Rabbits
A range-finding study was conducted in Chinchilla hybrid
rabbits (Becker et al. 1986a). Dams were administered either 0,
50, 150 or 300 mg/kg bw of technical triadimenol (purity 97.0%, A:B
= 80:20) on days 6 through 18 post-coitum (3 per dose level for all
groups although only one rabbit at the high dose level delivered
live fetuses). One dam died at high dose level. Salivation,
dyspnea and abnormal posture were observed in dams at the high dose
level. Slight decreases in body weight gain and food consumption
were noted in the low and mid dose levels (although not
dose-related). Weight loss was noted at the high dose level. Total
post-implantation loss was noted in one of the two surviving dams at
the high dose. One malformed dead fetus was found upon external
examination of the uterine contents from a dam at the 150 mg/kg bw
dose level. Visceral and skeletal examinations were not conducted.
In the primary rabbit teratology study, groups of Chinchilla
hybrid rabbits were administered by daily gavage either 0, 8, 40 of
200 mg/kg bw triadimenol technical (97% purity, A:B = 80:20) in
water with 0.5% cremophor as an emulsifier on days 6 through 18
post-coitum (Becker et al. 1986b). Rabbits had been naturally
mated and the day mating was observed was recorded as day 0
post-coitum. A total of 16 pregnant rabbits served as the control
population and 15 rabbits in each of the remaining groups. All
animals were weighed daily, food consumption was measured on days 6,
11, 15, 19, 24 and 28. Clinical observations were recorded at least
twice daily. On day 28 of gestation, all rabbits were sacrificed
and fetuses delivered by Cesarean section. All fetuses were
examined externally, viscerally and cleared, stained and examined
for skeletal anomalies. Dams were subject to gross pathologic
examination, the uteri weighed and numbers of corpora lutea and
resorptions were recorded.
Maternal toxicity was observed at 200 mg/kg bw in the form of
CNS stimulation one-half hour to 6 hours after dosing, local areas
of hair loss, decreased food consumption and body weight gain.
There were no mortalities in any group. A marginal decrease in body
weight gain was observed at 40 mg/kg day. No other effects
attributed to test compound were noted at this dose level or at
8 mg/kg bw.
Post-implantation loss was elevated at 200 mg/kg bw with the
percentage of resorptions increasing from 3.8% per dam in the
control population to 12.8% in the 200 mg/kg bw group. Slight
reductions were observed in group mean body weight and litter mean
body weight in the high dose group. No malformations or anomalies
were observed in the control fetuses. A total of 3 fetuses from 3
litters, 2 fetuses from the same litter and 7 fetuses from 7 litters
were diagnosed with a variety of developmental abnormalities,
consisting primarily of ossification defects in the sternebrae and
vertebrae. The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 8 mg/kg bw/day
based on slightly decreased weight gain. A teratogenic potential
was not observed at dose levels as high as 200 mg/kg bw/day. The
NOAEL for fetotoxicity was 40 mg/kg bw based on increased
resorptions.
A teratology study had been previously conducted using New
Zealand rabbits (Korte & Osterburg, 1980). Groups of animals were
naturally mated and after a positive vaginal smear (considered as
gestation day 0), animals received HCG. On days 6 through 18 after
mating, 0, 10, 30 or 100 mg/kg bw (purity 97%, A:B = 80:20) was
administered by oral gavage in a water vehicle with cremophor EL as
an emulsifier. Although between 18 and 21 rabbits were inseminated
in each group, only 13, 10, 10 and 11 rabbits delivered live
offspring in the 0, 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg dose groups (2 animals in
the low dose and one each at the mid and high dose had complete
mortality of the litter). Two high dose animals died during the
course of the study with postmortem evidence of pneumonia. Body
weights were measured on days 0, 6, 18 and 28. After sacrifice,
gross autopsy was performed on each maternal animal. The number of
corpora lutea, implantations, live and dead fetuses were recorded.
All fetuses were examined for external, visceral and skeletal
abnormalities.
Body weight was slightly (but significantly) decreased in
females at the high dose level during the period of days 6-18. No
other indications of toxicity were observed in the dams. No
malformations of any type were observed in any of the fetuses. A
high incidence (ranging from 83 to 90%) of minor skeletal variations
were observed in each group. There was no apparent compound effect
on the incidence or pattern of these variations. The NOAEL for
maternal toxicity is 30 mg/kg bw in this study. The NOAEL for
fetotoxicity/ teratogenicity is 100 mg/kg bw.
Observations in humans
A statement was submitted which noted that "no adverse effects
on production workers engaged in the manufacture of the
(triadimenol) have been observed by us" (Kollert, 1981). Another
statement noted "no cases of health impairment were observed by us
with the periodically medically supervised employees (males and
females) which are involved in the formulation of BAYTAN applying
the usual safety measures" (Miksche, 1981).
COMMENTS
The two optical isomers of this chemical are both rapidly
absorbed and excreted, with slightly more of each isomer excreted in
urine by males than females. Hydroxylation of the tert-butyl
moiety and subsequent oxidation to carboxylic acid is the primary
route of metabolism. Although one of the two specific isomers is
about 10 times more acutely toxic than the other, no differences in
short-term toxicity were found in tests of the 80:20 and 60:40
mixtures of isomers in rats.
Triadimenol has a low acute toxicity in the species examined.
Several short-term studies have been conducted in rats. At
higher doses increased liver weights and liver hypertrophy were
observed. The NOAEL was 120 ppm, equal to 8 mg/kg bw/day.
Three short-term dog studies have been conducted. The NOAEL
was 100 ppm in the diet (equal to 7.5 mg/kg bw/day) based on
hepatotoxicity at the higher dose levels.
A long-term toxicity study was conducted in mice. An increased
incidence of hyperplastic nodules in the liver was observed in
females at 2000 ppm (equivalent to 300 mg/kg bw/day). There was an
increased incidence of liver tumours in females at the 500 and
2000 ppm levels (equivalent to 75 and 300 mg/kg bw/day). A NOAEL
could not be established for this study since aspartate
amino-transferase was elevated in all treated groups in a
dose-dependent manner.
No increases in any tumour type were observed in a long-term
feeding study in rats. Hepatotoxicity was observed at 500 ppm and
above. The NOAEL was 125 ppm (equal to 7 mg/kg bw/day).
In a 2-generation, 2 litters per generation reproduction study
in rats, the NOAEL was 125 ppm in the diet, equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day.
Decreased parental pup body weights were observed at a dose level of
500 ppm. Teratology studies were conducted in rats and rabbits. An
increased rate of resorption was found at the high dose in the rat
study (120 mg/kg bw/day) and rabbit study (200 mg/kg bw/day). The
NOAELs for embry-fetotoxicity were 60 mg/kg bw/day in the rat and
40 mg/kg bw/day in the rabbit.
After reviewing all available in vitro and in vivo
short-term tests, the meeting concluded that there was no evidence
of genotoxicity.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat: 125 ppm in the diet, equal to 5 mg/kg bw/day (based
on reproductive effects)
Dog: 100 ppm in the diet, equal to 7.5 mg/kg bw/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for humans
0-0.05 mg/kg bw.
Studies which will provide information in the continued evaluation
of the compound
Observations in humans.
REFERENCES
Becker, H., Frei, D. & Sachsse, K. (1986a) Dose-finding
embryotoxicity including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rabbit. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R 3692.
Becker, H., Frei, D. & Sachsse, K. (1986b) Dose-finding
embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rabbit. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Unpublished Report No. R 3826
submitted to WHO by Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Becker, H., Frei, D., Vogel, W. & Terrier, C. (1987a)
Embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rat. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R3988.
Becker, H., Mueller, E., Vogel, W. & Terrier, C. (1987b)
Embryotoxicity (including teratogenicity) study with KWG 0519 in the
rat. RCC Itingen, Switzerland. Report No. R4145.
Bomhard, E. & Löser, E. (1982) KWG 0519 - Chronic toxicological
study on mice (feeding experiment over two years). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 10855.
Bomhard, E., Löser, E. & Schilde, B. (1979) 1,2,4-triazole.
Subchronic toxicological study with rats (feeding study over three
months). Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 8667.
Cifone, M.A. (1982) Mutagenicity evaluation of KWG 0519 in the
mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay. Litton Bionetics, Rockville,
Maryland. Report No. R 2204.
Flucke, W. (1981) KWG 0519 - Study of sensitization effect on
guinea pigs. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 9894.
Flucke, W. (1979a) KWG 0519 - Form A - Determination of acute
toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG.
Flucke, W. (1979b) KWG 0519 - Form B - Determination of acute
toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG.
Flucke, W. (1979c) KWG 0519 (Mixture of isomers) - Determination of
acute toxicity. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Heimann, K.G. (1985a) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13616.
Heimann, K.G. (1985b) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13617.
Heimann, K.G. (1985c) KWG 1640 N (Metabolite of KWG 0519) - Study
for acute oral toxicity to rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 13618.
Heimann, K.G. & Schilde, B. (1984) KWG 0519 - Subacute dermal
toxicity study on rabbits. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12496.
Herbold, B. (1981) KWG 0519 Triadimenol - The active ingredient of
Baytan. Study of DNA damage using the E. coli Pol-A1 test.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 102265.
Herbold, B. (1979a) KWG 0519 - Micronucleus test on mouse to
evaluate KWG 0519 for potential mutagenic effects. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 8584.
Herbold, B. (1979b) KWG 0519 - Salmonella/microsome test for
detection point -mutagenic effects. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer
AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 8189.
Herbold, B. (1978a) KWG 0519 - Dominant lethal study on male mouse
to test for mutagenic effects. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7900.
Herbold, B. (1978b) KWG 0519 - Micronucleus test on mouse to
evaluate KWG 0519 for potential mutagenic effects. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7588.
Hoffmann, K. & Vogel, O. (1984) KWG 0519 - First chronic study of
toxicity to dogs on oral administration (two-year feeding study).
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 12970.
Hoffmann, K. (1984) KWG 0519 - Second chronic study of toxicity to
dogs on oral administration (six-month feeding study). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12971.
Hoffmann, K. & Kaliner, G. (1977) KWG 0519 - Subchronic toxicity
study on dogs (thirteen-week feeding experiment). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6633.
Kimmerle, G. (1976) KWG 0519 - Subacute inhalation toxicity study
on rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 6321.
Kollert, W. (1981) BBA-requirement/effect on humans. Medical
Department EL, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Korte, R. & Osterburg, I. (1980) Embryotoxicity of KWG 0519 in
rabbits. Reprotox GmbH, Munster, FRG. Report No. R 1901.
Krötlinger, F., Löser, E. & Schilde, B. (1982) KWG 0519 - Chronic
toxicity study on rats (2-year feeding experiment). Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 11009.
Leeling, J.L., Helms, R.J., Polomcak, S.C. & Craigo, L.A. (1988)
Dermal absorption of triadimenol-14C in rats. Miles, Inc.,
Elkhart, Indiana. Report No. Mobay 1055.
Löser, E. & Kaliner, G. (1977) KWG 0519 - Subchronic toxicity study
on rats (three-month feeding experiment). Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6811.
Löser , E. & Eibenm R. (1984) KWG 0519 - Two-generation study on
rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG.
Report No. 12390.
Machemer, L. (1977) KWG 0519 - Evaluation for embryotoxic and
teratogenic effects on orally dosed rats. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 7038.
Mihail, F. & Vogel, O. (1981) Study of comparative toxicity to rats
after 4-week administration using two test compound samples.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 9949.
Mihail, F. & Thyssen, J. (1980) KWG 0519 - Acute toxicity studies.
Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report
No. 9451.
Polacek, I. (1983) Central nervous effects of KWG 0519 (Pilot
study). Toxicological Institute, Bayer AG, Regenburg, FRG. Report
No. 2695.
Puhl, R.J. & Hurley, J.B. (1978) The metabolism and excretion of
Baytan by rats. Mobay Chemical Company, Stilwell, Kansas. Report
No. 66489 (FM 209).
Putman, D.L. (1987) Sister chromatid exchange assay in Chinese
hamster ovary (CHO) cells. Microbiological Associates, Rockville,
Maryland. Report No. 1022.
Renhof, M. (1984) KWG 0519 - Study for embryotoxic effects on rats
after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer AG,
Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 12687.
Renhof, M. (1988a) 1,2,4-triazole - Investigations into embryotoxic
effects on rats after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 17402.
Renhof, M. (1988b) 1,2,4-triazole - Investigations into embryotoxic
effects on rats after oral administration. Institute of Toxicology,
Bayer AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 17401.
Tanahashi, N. & Moriya, M. (1982) Triadimenol - Microbial
mutagenicity study. Department of Toxicology, Institute of
Environmental Toxicology, Tokyo, Japan.
Thyssen, J. & Kaliner, G. (1976) KWG 0519 - Subacute oral
cumulative toxicity study on rats. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer
AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 6481.
Thyssen, J. & Kimmerle, G. (1976a) KWG 0519 - Acute toxicity
studies. Institute of Toxicology, Bayer, AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld,
FRG. Report No. 6090.
Thyssen, J. & Kimmerle, G. (1976b) 1,2,4-triazole. Institute of
Toxicology, Bayer, AG, Wuppertal-Elberfeld, FRG. Report No. 5926.
